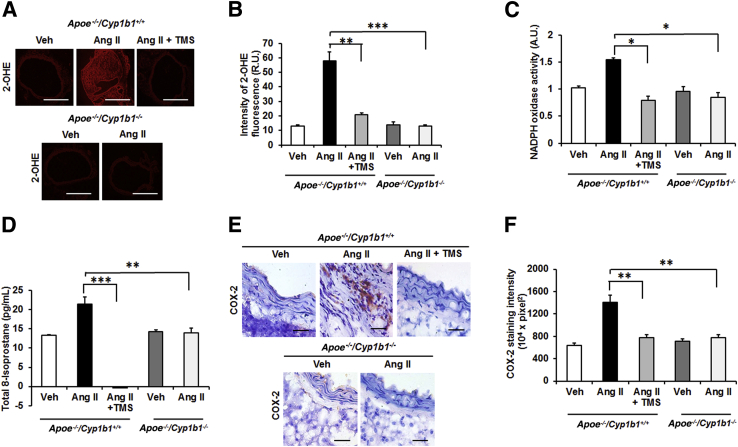
Figure 5.
2,3′,4,5′-Tetramethoxystilbene (TMS) treatment or Cyp1b1 gene disruption reduces oxidative stress in the aorta of Apoe−/−/Cyp1b1+/+ mice infused with angiotensin (Ang) II for 28 days. A and B: Photomicrographs of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production determined by 2-hydroxyethidium staining (A) and quantified as fluorescence of 2-hydroxyethidium (OHE) (R.U.) (B). C–F: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activity measured in heart homogenate (C); total 8-isoprostane level in the plasma (D); and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 staining (E), quantified as intensity of diaminobenzidine (F). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 5 per group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (two-way analysis of variance followed by the Bonferroni multiple-comparisons test). Scale bars: 50 μm (E, all groups); 200 μm (A, all other groups); 400 μm (A, Apoe−/−/Cyp1b1+/+ Ang II group). Original magnification: ×4 (A, Apoe−/−/Cyp1b1+/+ Ang II group); ×10 (A, all other groups); ×40 (E, all groups). A.U., arbitrary units; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; R.U., relative units; Veh, vehicle.