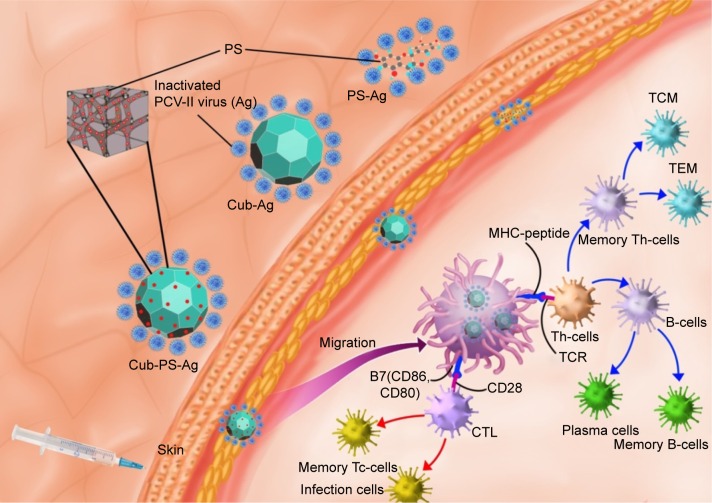
Figure 9.
The possible mechanism of Cub-PS action as vaccine adjuvants.
Notes: Cub-PS was mixed with inactivated PCV-II viruses and the Cub-PS-Ag formulation is formed. After subcutaneous injection of Cub-PS-Ag formulation, APCs, especially DCs located in the subcutaneous region, can phagocytose the Cub-PS-Ag, process the antigens during the migration to secondary lymph nodes, and become mature. At this moment, DCs present the MHC–peptide complex to T-cells at lymph nodes. CD80 and CD86 are highly expressed on the surface of DCs. Subsequently, some of the T- and B-cells become memory cells and protect the organism upon a second encounter with the same pathogen.
Abbreviations: Ag, antigen; CTL, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte; Cub-Ag, mixture of cubosomes and Ag; Cub-PS-Ag, mixture of cubosome-polysaccharide nanoparticles and Ag; DC, dendritic cell; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; PCV, porcine circovirus; PS-Ag, mixture of PS and Ag; TCM, central memory T-cells; TCR, T-cell receptor; TEM, effector memory T-cells; Th-cells, T-helper cells; Tc-cells, cytotoxic T cells.