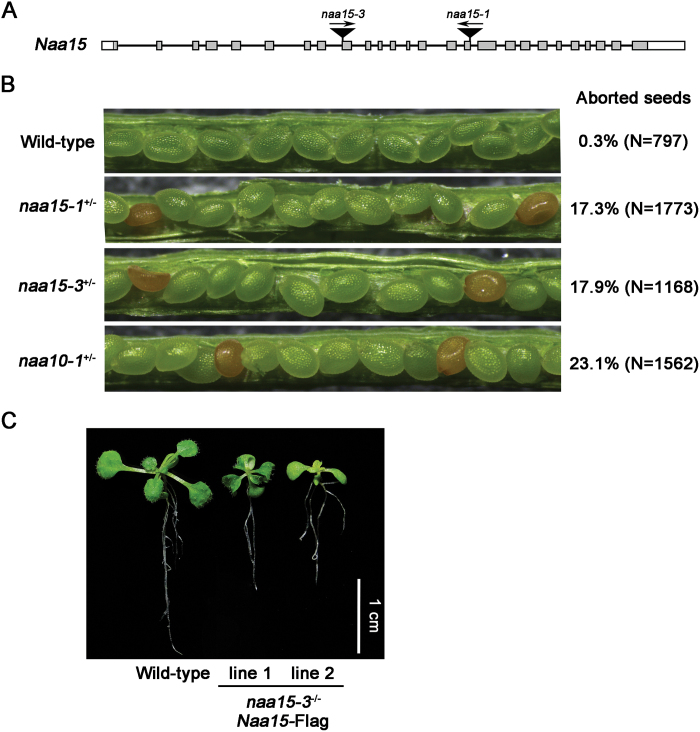
Fig. 5.
The mutation of Naa15 produced an embryo-lethal phenotype. (A) Schematic diagram of the two T-DNA insertions in Arabidopsis Naa15. The T-DNA insertions in naa15-1 (CS836292) and naa15-3 (CS24056) were in exons 16 and 9, respectively. Grey boxes indicate exons, black lines indicate introns, white boxes indicate UTRs. (B) Seed development in wild-type, naa15-1 +/–, naa15-3 +/–, and naa10-1 +/– plants. The ratios of aborted to normal seeds in siliques from wild-type, naa15-1 +/–, naa15-3 +/–, and naa10-1 +/– plants are shown. (C) Fifteen-day-old wild-type plants and naa15-3 –/– plants complemented with Naa15-Flag at the T1 generation. The Naa15 CDS fused to 3xFlag driven by its native promoter was cloned into pCambia1300. The resulting pNaa15::Naa15-Flag plasmid was introduced into naa15-3 +/– by A. tumefaciens-mediated transformation. T1 plants were selected using hygromycin and Basta, and then genotyped by PCR. Lines 1 and 2 are independent naa15-3 –/–-complemented lines.