Figure 3.
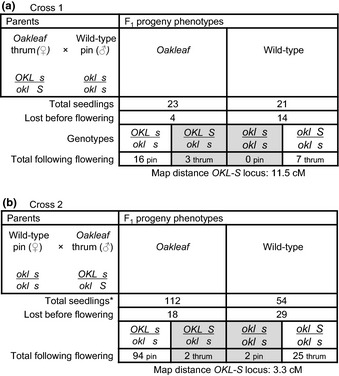
Genetic analysis of reciprocal crosses between Primula vulgaris Oakleaf and wild‐type plants. The results of reciprocal crosses between a P. vulgaris Oakleaf thrum and a wild‐type pin plant are shown. (a) Cross 1, Oakleaf as female parent. (b) Cross 2, Oakleaf as male parent. The phenotypes and genotypes, with respect to leaf shape (wild‐type or Oakleaf), and the S locus (pin or thrum) of parent plants are indicated. The phenotypes, and predicted genotypes, of F1 progeny are shown, along with numbers of progeny classified initially only with respect to leaf shape. The number of each class of progeny lost before flowering is shown, as well as the number of pin‐ and thrum‐type flowers found on Oakleaf and wild‐type plants. Oakleaf (OKL) is shown in coupling to the recessive s allele of the S locus in the original plant based on the assumption that minor progeny classes represent recombinants; genotypes of recombinant chromosomes in progeny and numbers of recombinant progeny are shaded grey. *Does not include 45 seedlings that died before forming secondary leaves.
