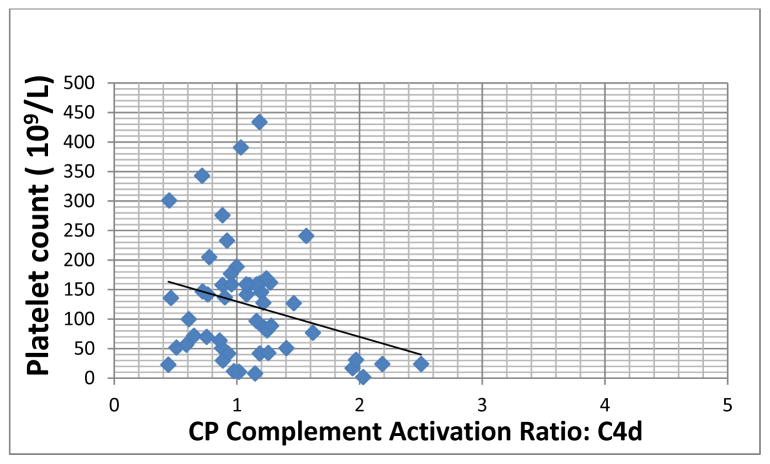
Figure.
Correlation between classical pathway (CP) complement activation, represented here by C4d deposition, and platelet count (Advia 2120, Siemens Healthcare Systems, Tarrytown, NY) in patients with chronic ITP. CP activation is expressed as a ratio relative to baseline complement activation observed using normal donor plasma. A ratio of >1.5, representing >3 S.D. from the reference range, was considered positive. (Correlation coefficient, r2= −0.414, p= 0.042).
Blood was obtained during patient clinic visits, using vacutainer tubes containing 3.2% sodium citrate (blood: anticoagulant ratio 1:10) (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). Platelet free plasma was prepared within 60 min of blood collection by centrifugation (1000g, 20 min, room temperature), aliquoted, and frozen at −80C until testing. CP activation was evaluated using a previously described assay (Peerschke, et al 2009) in which immobilized heterologous platelets are exposed to patient plasma or normal pooled control plasma (George King Bio-Medical, Inc, Overland Park, KS), and complement deposition is measured using monoclonal antibodies to C1q, C4d, C3b and C5b-9 (Quidel Corp., Santa Clara, CA).