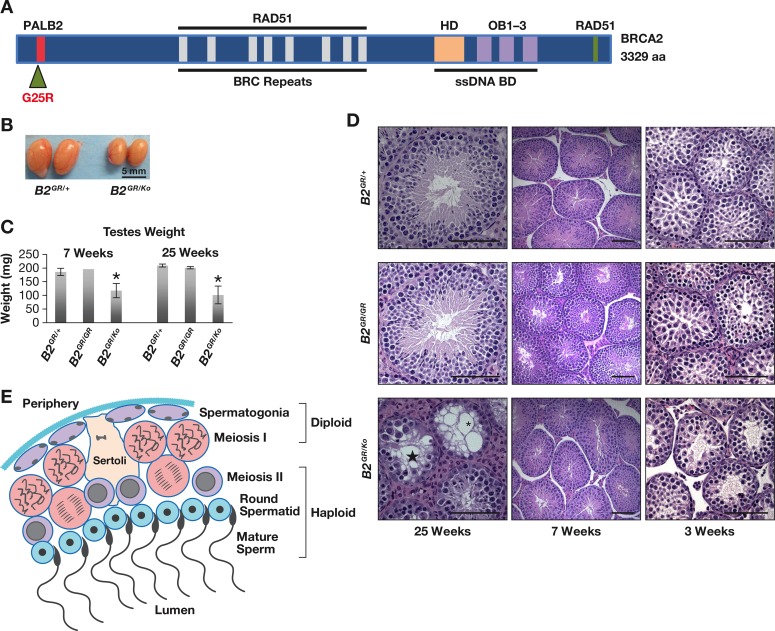
Fig 1. Brca2G25R/Ko mutant males have decreased fertility.
A. Structural and functional domains of murine BRCA2 consisting of 3329 amino acids with the N-terminal PALB2 binding domain (red), BRC repeats (gray) in the middle, helical domain (HD, orange), oligonucleotide binding (OB) regions 1–3 (purple), and a C-terminal RAD51 binding domain (green). Single-strand DNA binding domain (ssDNA, line). The dark green triangle marks the location of the G25R mutation. B. Representative images of mouse testes of indicated genotype (B2GR/+, left and B2GR/Ko, right) at 25 weeks of age. C. Average paired testes weight (mg) of the listed genotypes at 7 weeks and 25 weeks, error bars indicate SD. * p<0.05. D. Representative H&E stained histology of testes of the indicated genotypes (B2GR/+, upper, B2GR/GR, middle, and B2GR/Ko, lower) at 25 weeks (tubules lacking germ cells (*), and tubules arrest at meiosis (star), 7 weeks with normal spermatogenesis, and 3 weeks, with reduced haploid cells in B2GR/Ko testis sections. E. Cartoon of a portion of mouse adult seminiferous tubule cross-section showing spermatozoa at various developmental stages from periphery (top) to lumen (bottom). Scale Bar = 100 μM. Controls are represented by either: Brca2+/+, Brca2Ko/+, or Brca2G25R/+. Abbreviations: Brca2G25R/+ = B2GR/+, Brca2G25R/G25R = B2GR/GR, Brca2G25R/Ko = B2GR/Ko.