Figure 4. Positions and interactions of the N-terminal domains of RelA.
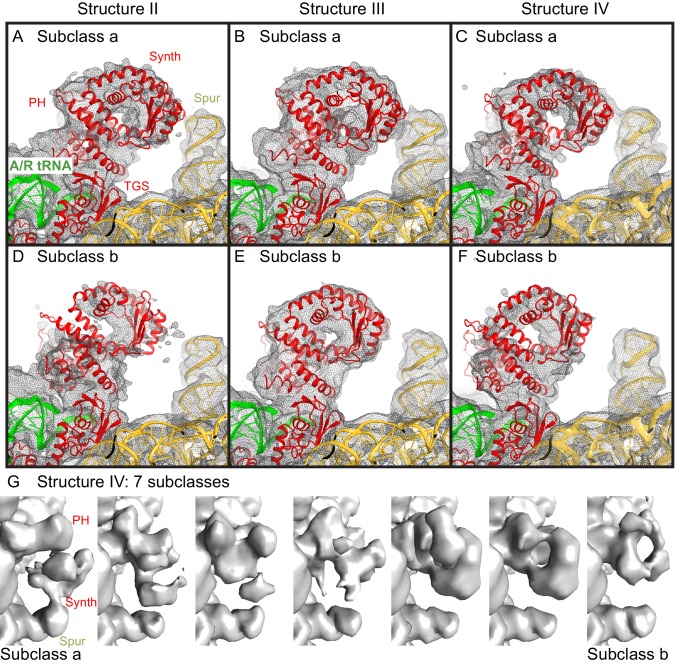
(A) Pseudo-hydrolase (PH; pink) and synthetase (Synth; red) domains are in the intersubunit space between the sarcin-ricin loop (SRL) of the 23S rRNA and the spur of the 16S rRNA. The N-terminal domains are shown in a conformation, in which the synthetase domain is near the spur (Structure IV is shown). (B) Comparison of the two conformations of the N-terminal domains inferred from the heterogeneous cryo-EM density by additional sub-classification (Structure IV is shown; see also Figure 4—figure supplement 1). The red model is shown as in (A). The gray model exhibits a conformation shifted away from the spur. (C) Relative positions of the synthetase domain and the spur in Structure IVa. (D) Structure of the innate immune sensor OAS1 (blue, PDB: 4RWP) bound with an RNA helix (magenta) (Lohöfener et al., 2015). OAS1 is a second-messenger-(2′-5′-oligoadenylate)-synthesizing enzyme, whose architecture resembles that of the synthetase domain of RelA, shown in a similar orientation in (C). The nucleotide-binding loop (NB loop) and other structural elements are labeled.