Figure 2.
Analysis of Ttc25 Mutant Mice and Ttc25 Knockdown in Xenopus
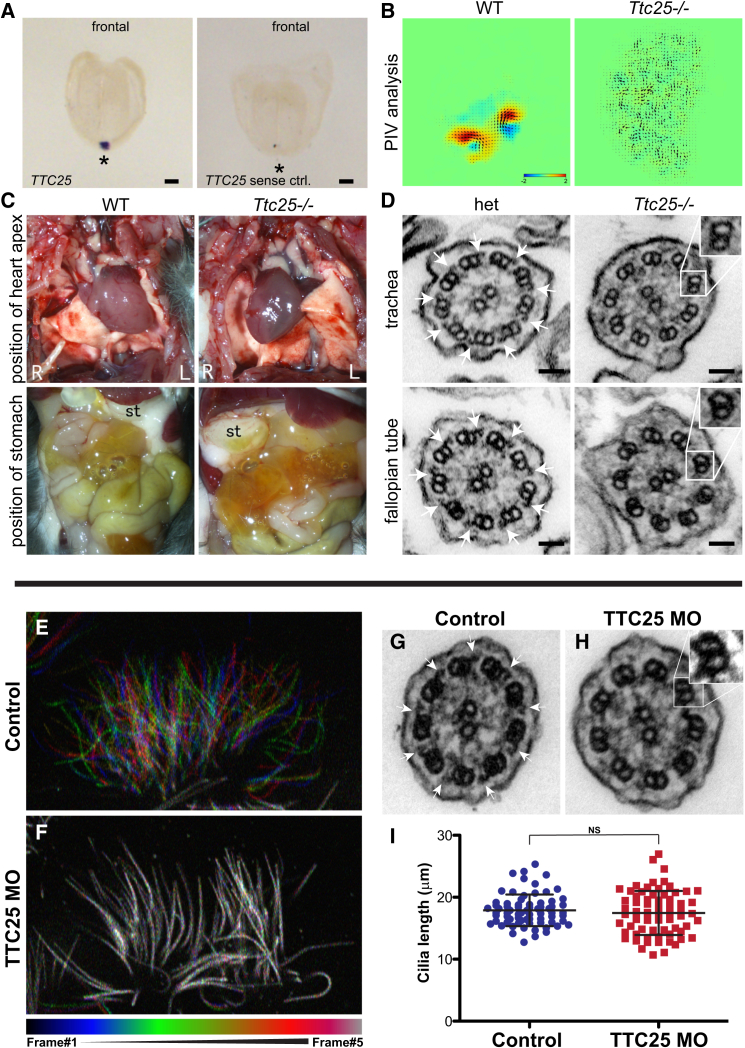
(A) In situ hybridization analyses of wild-type mouse embryos at the age of embryonic day (E) 7.5 revealed strong and restricted expression of Ttc25 at the ventral node (asterisk). A sense probe was used for negative controls, which do not show any signal (right).
(B) Particle image velocimetry (PIV) analysis of the ventral node also revealed differences between wild-type (WT) and mutant embryos. Whereas, at the wild-type node, flow of particles is rapid and directed, for the Ttc25 mutant embryo, only scattered and undirected movement could be observed. Leftward flow is shown in yellow and red and rightward in blue.
(C) Mice carrying the Ttc25 mutation show randomization of left-right body asymmetry. In wild-type mice, the heart apex points to the left side (top left). In mutant mice, shown here, it points to the right side (dextrocardia) (top right). The stomach (st) is localized on the left side in wild-type animals (bottom left), but was found on the right side in Ttc25 mutants (bottom right).
(D) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of ciliary cross-sections from the trachea (upper panel) or fallopian tubes (lower panel) of a heterozygous (het) Ttc25 mutant mouse (left column) revealed the presence of ODAs (white arrows) attached to the A tubules. In homozygous Ttc25 mutant mice (right column), the ODAs are lacking.
(E and F) Color-based time coding of time-lapse data from high-speed confocal microscopy reveals robust beating in control multiciliated cells of Xenopus (E), and a failure of beating in Ttc25 morphants (F). Colored bar below indicates the color of each of five frames in the time-lapse movie.
(G–I) ODAs are apparent in TEM of normal axonemes of Xenopus multiciliated cells (G), but are absent in axonemes after Ttc25 knockdown (H). At the stages examined here, Ttc25 knockdown has no effect on cilium length (I).
Scale bars represent 100 μm (ISH) and 5 nm (TEM).