Figure 2. Effect of lithium therapy on urinary ammonia excretion in response to an acute acid load in humans.
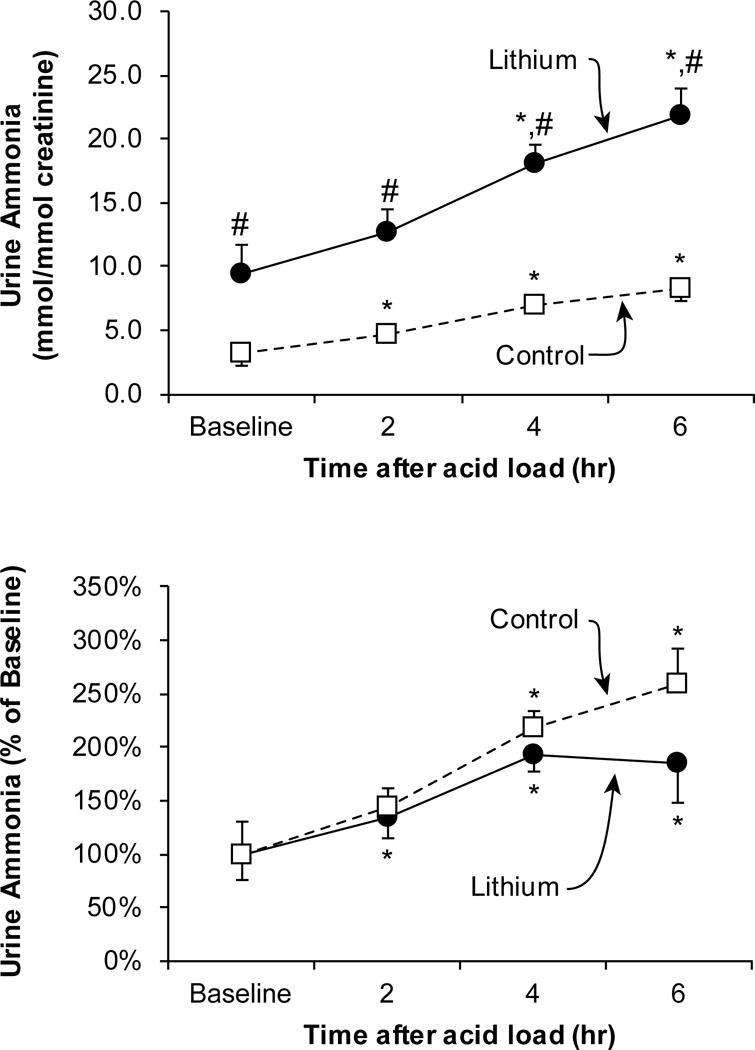
Top panel shows urinary ammonia excretion, expressed as mmol per mmol creatinine, at baseline, and following an acute acid load. Baseline urinary ammonia excretion was significantly higher in lithium-treated subjects than in control subjects. An acute acid load, induced by oral ammonium chloride loading, resulted in significant increases in urinary ammonia excretion in both groups at each time point. However, at each time point, urinary ammonia excretion was significantly greater in lithium-treated subjects than in control subjects. Bottom panel shows changes in urinary ammonia excretion relative to adjusted for baseline urinary ammonia excretion rates. An acute acid load resulted in significant increases in ammonia excretion relative to baseline excretion in both groups. *P < 0.05 versus baseline; #P < 0.05 versus control at same time point. Figure from [17], and used with permission.
