Fig. 9.
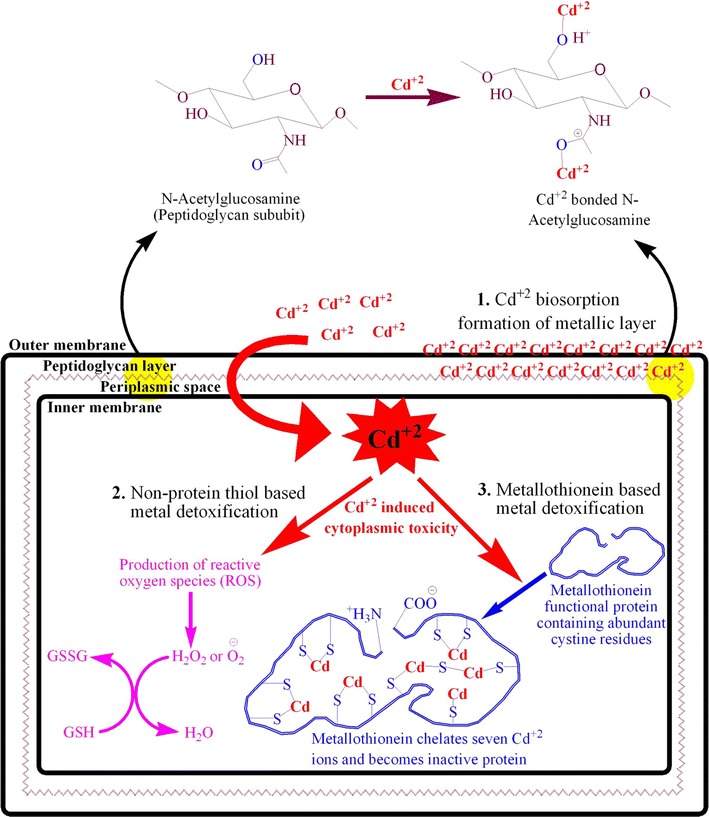
Proposed Cd2+ biosorption and resistance mechanism in gram negative bacterium, S. enterica 43C. (1) Peptidoglycan is the primary site on bacterial surface that binds Cd2+ in monolayer. (2) Cd2+ enter the cells via metal ions transport channel proteins and are known to cause oxidative stress which is combated by GSH dependent antioxidant system. (3) Metallothioneins, induced by Cd2+ stress, are primarily involved in Cd2+ sequestration through their thiols groups thus mitigating Cd2+ interference with cellular metabolism
