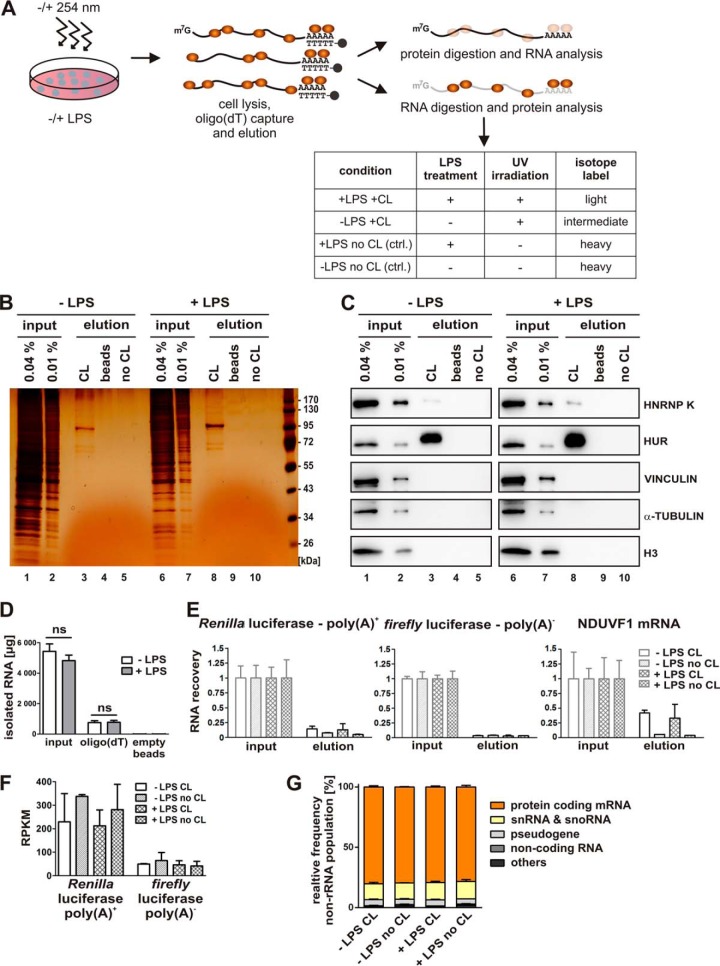
Fig. 1.
RBP enrichment by in vivo UV-crosslinking and oligo(dT) capture. A, Experimental design. RAW 264.7 cells were either left untreated or induced with 10 ng/ml LPS for 2 h and subsequently UV-irradiated (λ = 254 nm) (crosslinked, CL) to stabilize RNA-protein interactions. To enrich poly(A)+ RNA, RNA-protein complexes were subjected to oligo(dT) capture after cell lysis and eluted, treated either with proteinase K to purify the RNA or with RNase A/T1 for Western blot analysis and mass spectrometry. B and C, Following RNase A/T1 digestion, released proteins were analyzed by silver staining (B, lanes 1–10) or with antibodies specific for known RBPs (HNRNP K and HUR) or control proteins (VINCULIN, α-TUBULIN and histone H3) (C, lanes 1–10). Beads lacking oligo(dT) (beads) or preparations from non-UV-irradiated cells (no CL) served as controls. D, Total amounts of isolated RNA from input and elution from oligo(dT)- and empty magnetic beads. E, QPCR analysis of RNA isolated from the input and the oligo(dT)-bound fraction following proteinase K treatment of the beads, performed in triplicates. Equal proportions of the input and eluate samples were used for qPCR analysis. Primers against spike-in controls, which were added prior to oligo(dT) capture, polyadenylated Renilla luciferase mRNA (Renilla poly(A)+), nonadenylated firefly luciferase mRNA (firefly poly(A)−) or endogenous NDUFV1 mRNA were used. F, Quantification of Renilla luciferase-poly(A)+ and firefly luciferase-poly(A)− from high throughput sequencing of eluted RNAs. Raw read counts were normalized for total read length and the number of sequencing reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM). G, High throughput sequencing of eluted RNAs. The percentage of non-rRNA reads mapped to the mouse transcriptome is displayed. Noncoding RNAs comprise miRNAs, lncRNAs and asRNAs.