FIGURE 6.
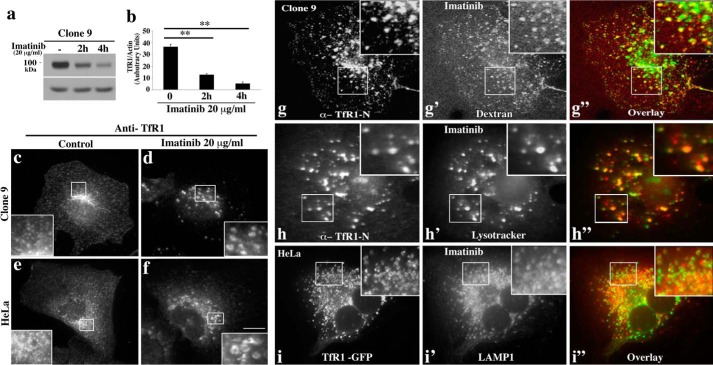
TfR1 is targeted to the lysosome in response to c-Abl inhibition. a, treatment of clone 9 cells with imatinib causes a loss of total TfR. Clone 9 cells treated with 20 μg/ml imatinib over different time periods (0, 2, and 4 h) were subjected to Western blotting analysis using an antibody to TfR1. A dramatic and stepwise reduction of TfR1 levels was observed resulting in an almost complete loss of the receptor by 4 h post-treatment as confirmed by densitometric quantitation of three different experiments. b, **, p < 0.01. c–f, immunofluorescence images of clone 9 or HeLa cells under control conditions (c and e) or treated with 20 μg/ml imatinib for 2 h (d and f). Control cells show a punctate endosomal plasma membrane-associated as well as the typical peri-nuclear pool of the TfR1. In contrast, imatinib-treated cells sequestered the TfR1 into large circular structures often with a dark unstained center (d and f; insets). g–g″, TfR1 resides in dextran-positive endosomes in imatinib-treated cells as visualized after pulse-chase labeling of endosomes and costaining of endogenous TfR1. h and h′, clone 9 cells were pre-treated with LysoTracker Deep Red (1 μm) in medium for 1 h. TfR1 resides in LysoTracker-positive compartment in imatinib treated cells as visualized by staining of endogenous TfR1. i–i″, imatinib-treated HeLa cells expressing GFP tagged TfR1 (i) were analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence using an antibody against the lysosomal marker LAMP1 (i′). An obvious co-labeling of TfR1 with late endosomes/lysosomes is observed (i–i″), indicative of receptor “mis-sorting” to the lysosome upon inhibition of c-Abl kinase. Scale bars, 10 μm.