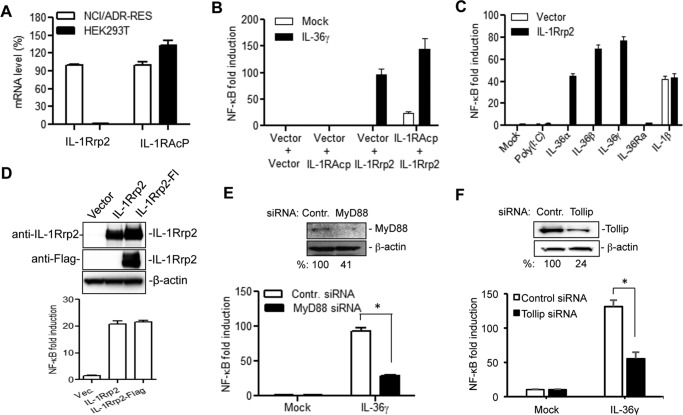
FIGURE 2.
A cell-based reporter assay to examine the function of IL-1Rrp2 in IL-36R signaling. A, HEK human embryonic kidney 293T cells express an undetectable level of IL-1Rrp2. The mRNA levels of IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP in 293T cells were quantified using real-time RT-PCR and adjusted to the levels from NCI/ADR-RES cells. The data were normalized to the GAPDH mRNA control from each sample. B, transfection of IL-1Rrp2 plasmid triggered NF-κΒ promoter activation upon IL-36 agonist addition. 293T cells were transfected to express IL-1Rrp2 and reporter constructs and then mock-treated or stimulated with 2 ng/ml of IL-36γ overnight. The luciferase activities are plotted as fold induction relative to cells transfected with the vector. The white and black bars denote the mock-treated and IL-36γ-stimulated activity. All results shown represent the means and standard deviations from at least three independent samples. C, effects of different ligands on the NF-κΒ activity in cells transfected to express IL-1Rrp2. D, effect of a FLAG-tagged IL-1Rrp2 on protein accumulation and signal transduction in 293T cells. Equal amounts of IL-1Rrp2 and FLAG-tagged IL-1Rrp2 plasmids were transfected into 293T cells, and the protein level was determined by Western blotting analysis probed with either goat anti-IL-1Rrp2 or rat anti-FLAG antibody. The NF-κΒ activation was determined as described above. E, siRNA knockdown of endogenous MyD88 in 293T cells significantly decreased IL-36γ mediated NF-κB activation. 293T cells were first transfected with 40 nm of either control siRNAs or MyD88 siRNAs for 48 h and then transfected to express IL-1Rrp2 for 24 h. The cells were mock-treated or treated with 2 ng/ml of IL-36γ. A significant reduction of MyD88 protein by the siRNA knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting analysis. The asterisk denotes that the two samples differed by a p value of < 0.05 in the Student's t test. F, effect of knockdown of endogenous Tollip on IL-36R signaling.