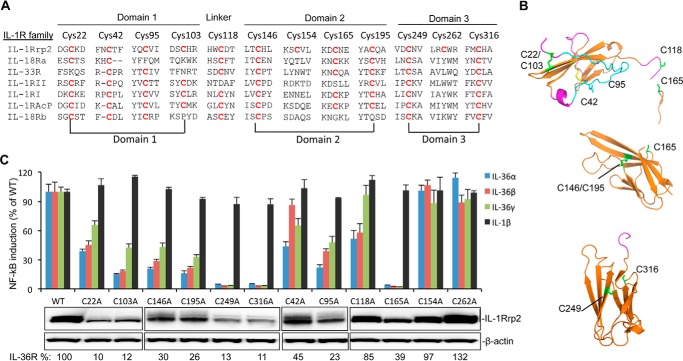
FIGURE 3.
Effects of cysteine to alanine substitutions in the IL-1Rrp2 ectodomain on protein accumulation and signaling. A, sequence alignment of cysteine residues in the IL-1R family. The IL-1Rrp2 ECD sequence is shown on the top, and residues in the IL-1R family that have conserved cysteine are marked in red. Cys pairs that are predicted to form disulfide bonds are connected by lines below the sequences. B, molecular model of potential disulfide bonds in three Ig-like domains of IL-1Rrp2. The cysteine residues, including the side chains, are in green. C, effects of cysteine mutations on IL-36R signaling and protein expression. Equal amounts of either WT IL-1Rrp2 or mutants were transfected into 293T cells along with the reporter plasmids as described. The cells were mock-treated or stimulated with 2 ng/ml of either IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ, or IL-1β. The data were plotted relative to WT IL-1Rrp2 and expressed as a mean of three independent samples and the range for standard error. The levels of accumulated WT IL-1Rrp2 and cysteine mutants were determined by Western blotting analysis. β-Actin from each sample was detected as a loading control. The relative amount of protein was quantified by ChemiDoc software (Bio-Rad).