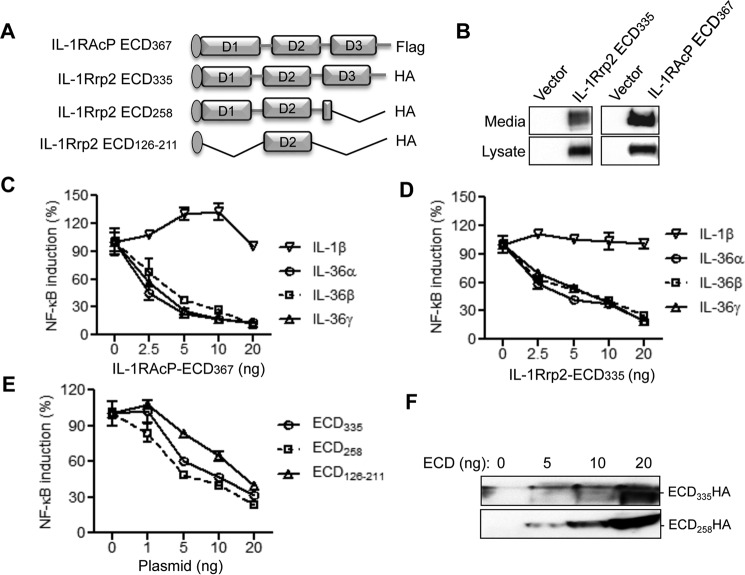
FIGURE 7.
Overexpression of ECDs of IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP exhibit dominant-negative effect on IL-36R signaling. A, schematic of ECDs of IL-1RAcP and IL-1Rrp2. The IL-1RAcP ECD367 contains the signal peptide at the N terminus and a FLAG tag at the C terminus, whereas the full-length and truncated IL-1Rrp2 ECDs contain the HA tags at the C terminus of the constructs. B, transient expression of IL-1RAcP ECD367 and IL-1Rrp2 ECD335. Western blotting analysis shows the abundances of ECD335 in the cell lysate and in the medium of cell culture. C, overexpression of IL-1RAcP ECD367 can inhibit IL-36R signaling induced by IL-36 cytokines. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with constant amount of IL-1Rrp2 plasmid along with increasing concentrations of IL-1RAcP ECD367. The cells were then treated with 2 ng/ml of either IL-1β, IL-36α, IL-36β, or IL-36γ and the data were plotted as percent of IL-1RAcP ECD367 mock-transfected control. D, overexpression of ECD335 inhibits IL-36R signaling induced by IL-36 cytokines. E, effects of expression of IL-1Rrp2 ECD258 and ECD126–211 on IL-36R signaling. F, levels of IL-1Rrp2 ECD335 and ECD258 in the culture medium. The secreted ECDs in medium were detected as input control.