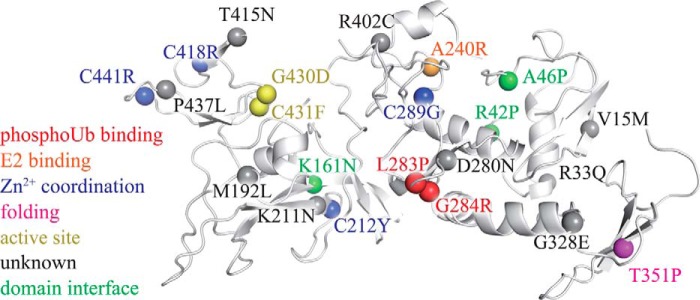
FIGURE 9.
AR-JP mutations may unbalance the conformational dynamics of parkin by a variety of mechanisms. Pathogenic mutations linked to autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism (3, 30, 54–62) are mapped onto the crystal structure of parkin (spheres). Several mutants appear to affect the structure of parkin by interfering with Zn2+ binding (blue) or the correct formation of secondary structure elements (magenta). The mutants G430D and C431F directly affect the active site (yellow). Other PD mutants may alter domain-domain interactions (green). Ala240 (orange) is critical for binding to the E2, and Leu283 and Gly284 (red) participate in phosphoubiquitin binding (19). Many of the remaining PD mutants are less well understood (gray) but may modulate the overall conformational dynamics of the enzyme. The structure of parkin was drawn from PDB code 4K95 (7).