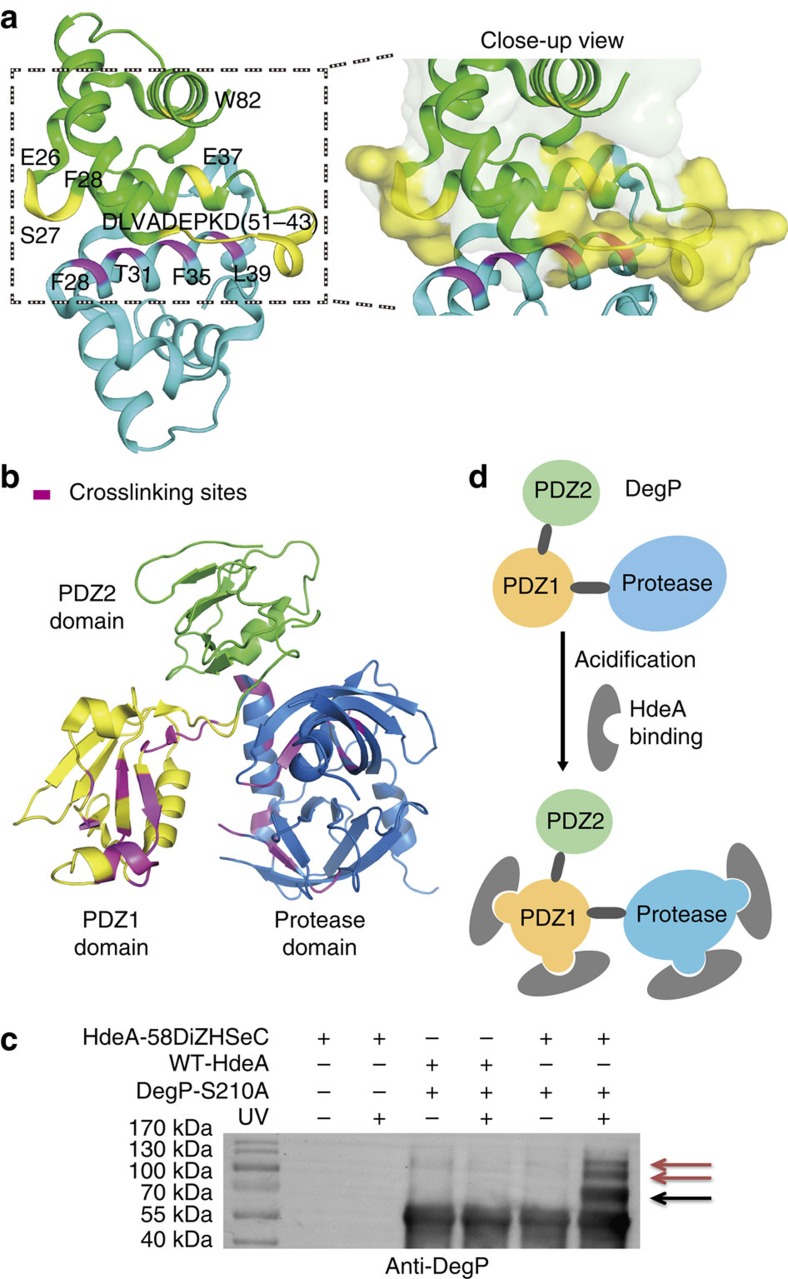
Figure 5. Mapping protein–protein interaction interface using IMAPP.
(a) Mapping of HdeA dimer interface using the IMAPP strategy. DiZHSeC was incorporated at different sites (F28, T31, F35 and L39), respectively, on HdeA to photocrosslink with WT-HdeA at pH 7. The incorporation sites of DiZHSeC (coloured in magentas) and the crosslinking sites (coloured in yellow) are displayed on the crystal structure of HdeA (PDB: 1DJ8; ref. 28). The bait HdeA is coloured in cyan and the crosslinked HdeA is coloured in green. Close-up view of the crosslinking interface is shown in the left. Crosslinked HdeA monomer is shown as a surface representation with crosslinking residues coloured in yellow and the other residues coloured in green. (The representative result from three replicates is shown). (b) Interaction interface of HdeA-DegP mapping through the photocrosslinking sites identified by IMAPP strategy. The crystal structure of DegP (PDB: 3MH4; ref. 34) contains a protease domain (coloured in blue) and two PDZ domains (colour in yellow and green, respectively). Based on the integrated crosslinking sites identified by IMAPP (coloured in magenta), the HdeA–DegP interface can be mapped to the protease domain and the PDZ1 domain (The representative result from two replicates is shown). (c) Multiple HdeAs may bind to a single DegP molecule under acidic conditions. HdeA-V58DiZHSeC or WT-HdeA was used to photocrosslink with DegP-S210A and the crosslinked complexes were analysed by immunoblot. The crosslinked complex with a ratio of 1:1(HdeA/DegP) binding is marked with a black arrow. Crosslinked complexes with higher HdeA/DegP binding stoichiometries are marked with red arrows. (The representative result from three replicates is shown). (d) A proposed model illustrating that HdeA may interact with different regions on DegP while multiple HdeA chaperone molecules may also simultaneously bind to the same DegP molecule under acid stress.