Figure 7.
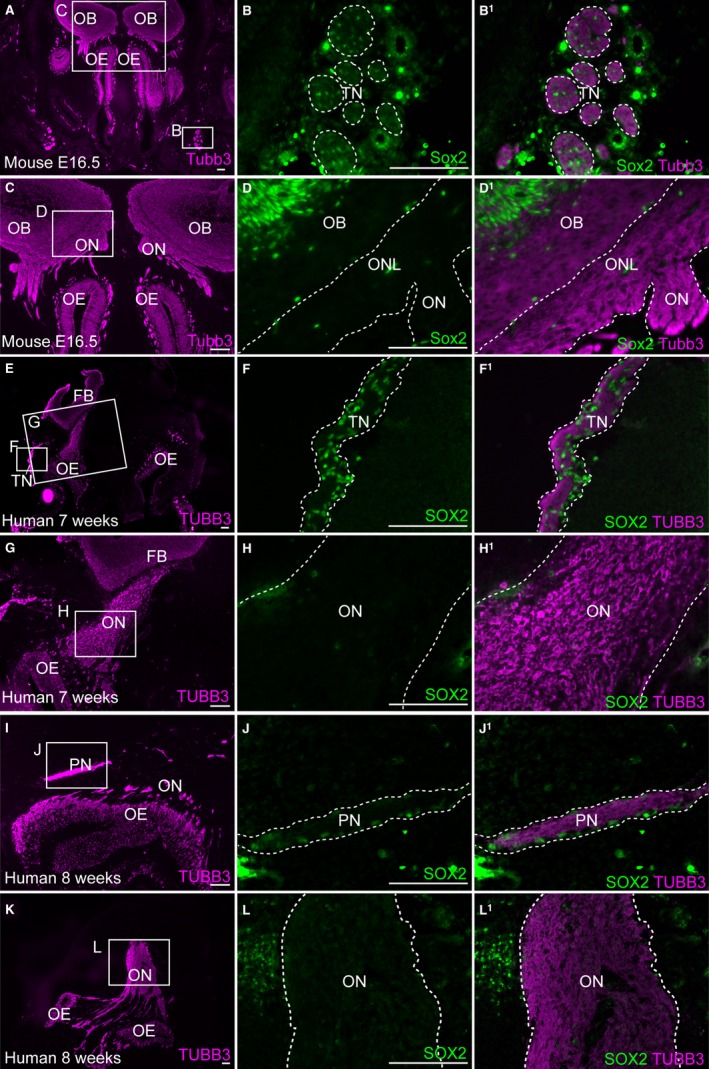
Embryonic human and mouse OECs do not express the Schwann cell precursor and immature Schwann cell marker Sox2. Coronal sections of the embryonic mouse (A–D1) and human (E–L) olfactory systems. (A) At E16.5 in the mouse, immunostaining for Tubb3‐positive axons provides an overview of the olfactory system. (B,B1) Higher‐power view of boxed region in (A), showing Sox2 expression in cells associated with Tubb3‐positive trigeminal axons, presumably developing Schwann cells. (C–D1) In contrast, on the same section shown in (A–B1), Sox2 is not expressed by OECs in the olfactory nerve layer of the olfactory bulb, or on the olfactory nerve. (E–F1) At 7 weeks of human development, SOX2 is strongly expressed by cells on the TUBB3‐positive trigeminal nerve, presumably developing Schwann cells, but (G–H1) SOX2 is not expressed by developing OECs on the olfactory nerve. (I–J1) Similarly at 8 weeks of human development, SOX2 is detected in developing Schwann cells, but (K–L1) is absent or expressed at very low levels in OECs on the same section. FB, forebrain; OB, olfactory bulb; OE, olfactory epithelium; ON, olfactory nerve; ONL, olfactory nerve layer; PN, peripheral nerve; TN, trigeminal nerve. Scale bar: 100 μm.
