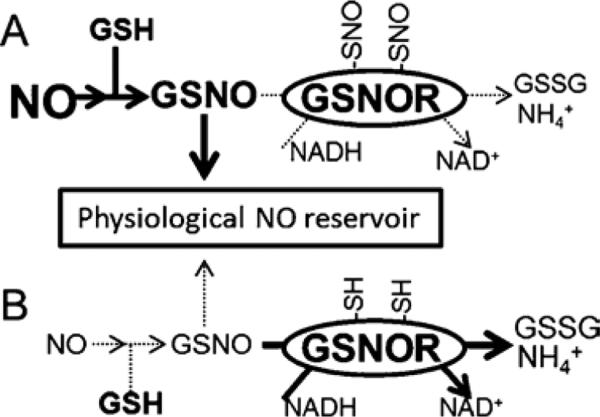
Figure 7. A model for the function of reversible GSNOR nitrosation.
A: During a nitric oxide burst, GSNOR is nitrosated on conserved cysteines, leading to a decrease in enzymatic activity. Lower GSNOR activity facilitates accumulation of GSNO, itself an agent of protein nitrosation. By allowing GSNO to accumulate, down-regulation of GSNOR permits robust nitric oxide signaling. B: Eventually GSNOR is re-reduced by cellular antioxidant machinery, whereupon GSNO concentrations are returned to basal levels by GSNOR.