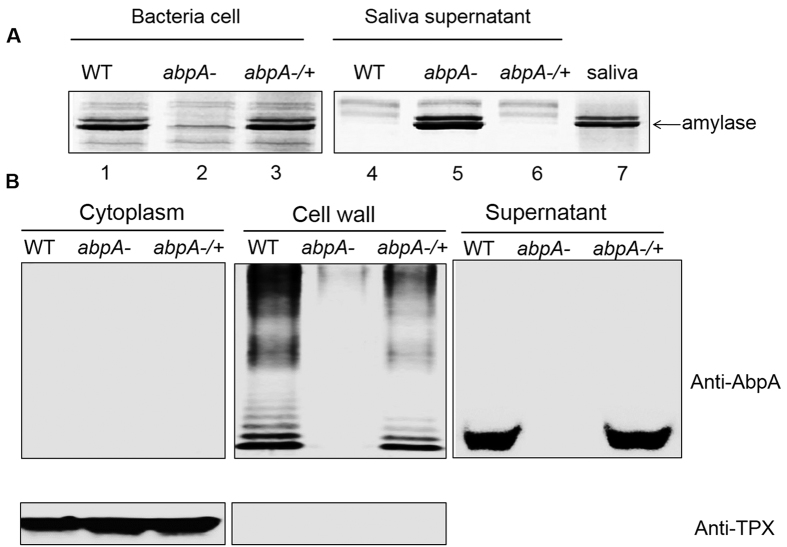
Figure 1. AbpA binds to amylase and is anchored to the bacteria cell wall.
(A) abpA mutation abolished amylase binding. Bacterial cells harvested from S. parasanguinis wild-type strain, abpA mutant and the complemented strain (abpA−/+) were incubated with saliva for amylase binding assay. The intact bacterial cells (left) were separated from saliva supernatants (right), and subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis and protein staining. An arrow labels amylase. (B) AbpA is anchored to the cell wall. Subcellular fractionation was prepared from S. parasanguinis wild-type strain, abpA mutant and the complemented strain (abpA−/+) and examined by Western blot analysis using anti-AbpA antibody. TPX, a cytoplasmic protein, was used as a control.