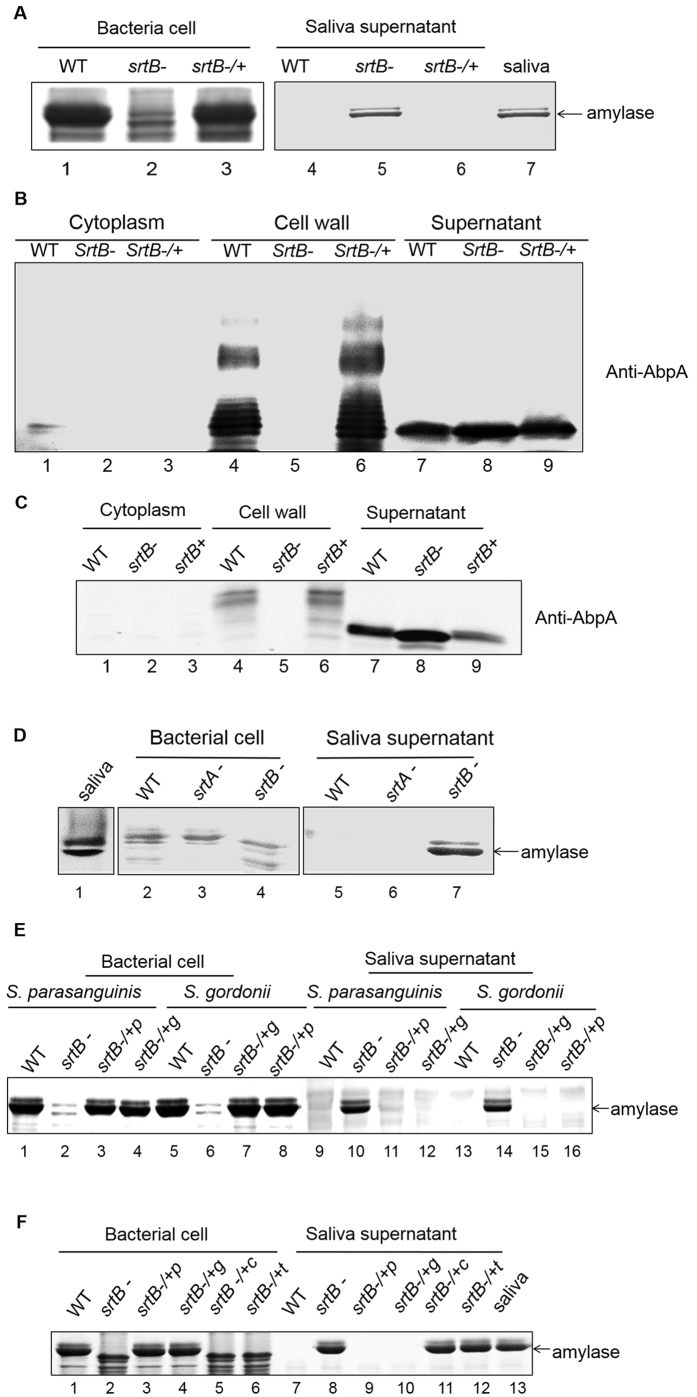
Figure 2. SrtB mediates the cell surface localization of AbpA and amylase binding.
Amylase binding to bacterial cells was performed as described in Fig. 1. Amylase bound to the bacterial cells (left) and remained in the saliva supernatants (right) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue protein staining. (A) srtB mutation abolished amylase binding. (B) S. parasanguinis and (C) S. gordonii srtB mutation abolished the cell wall display of AbpA. Subcellular fractions of wild-type strain, srtB mutant and the complemented strain were subjected to Western blot analysis with corresponding anti-AbpA antibody. (D) srtA mutation did not affect amylase binding. (E) Cross-complementation between S. parasanguinis SrtB and S. gordonii SrtB. Amylase was indicated by an arrow. +p, from S. parasanguinis; +g, from S. gordonii. (F) SrtB from S. aureus (srtB −/+c) and S. pneumoniae (srtB −/+t) cannot restore amylase binding of srtB mutant from S. parasanguinis. +p, from S. parasanguinis; +g, from S. gordonii; +c, from S. aureus; +t, from S. pneumoniae.