Fig. 1.
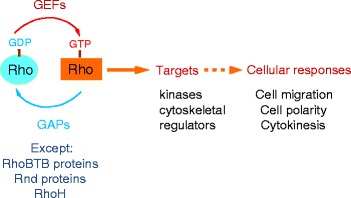
Regulation of Rho GTPases. Most Rho GTPases cycle between an inactive GDP-bound conformation and an active GTP-bound conformation. When bound to GTP, they interact with downstream target proteins to induce cellular responses, for example, cell migration, cell polarity and cytokinesis. They are activated by exchange of GDP for GTP, which is stimulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). They are inactivated by GTP hydrolysis, which is catalysed by GTPase-accelerating factors (GAPs). Exceptions are the Rho family members RhoBTB proteins (RhoBTB1, RhoBTB2), Rnd proteins (Rnd1, Rnd2, Rnd3) and RhoH, which have amino acid substitutions that prevent GTP hydrolysis and, hence, are constitutively GTP-bound
