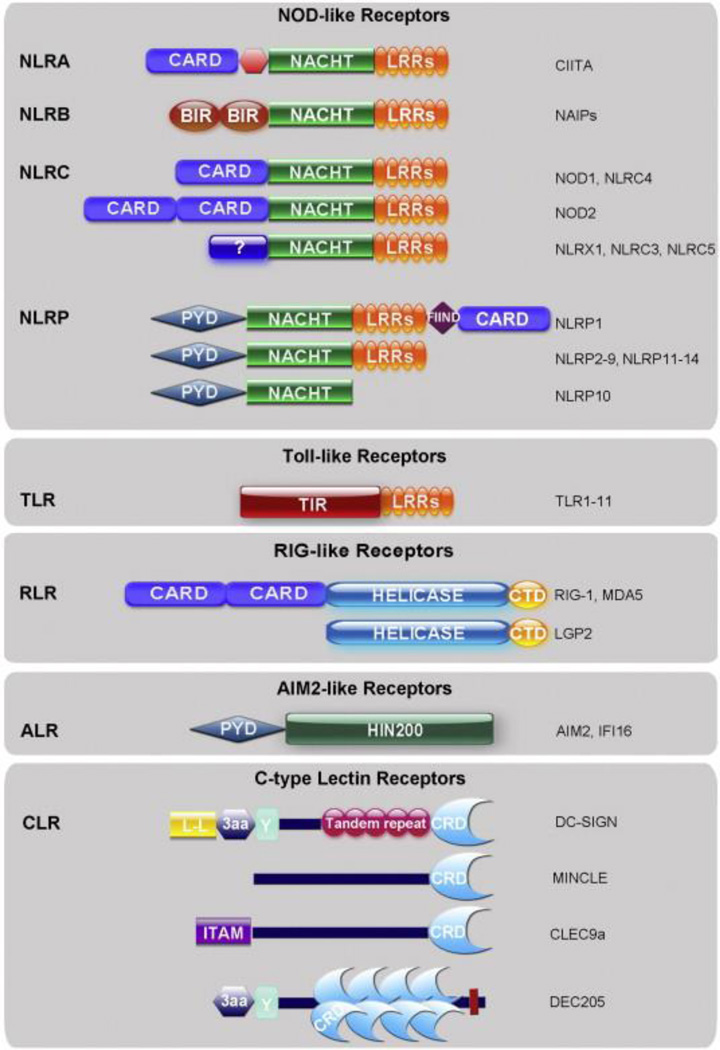
Fig. 1.
Structural domains of pattern recognition families. The major structural domains of TLRs, NLRs, RLRs, ALRs, and CLRs are depicted above. Note that the NLR family is divided into 4 subfamilies: NLRA, NLRB, NLRC and NLRP. CLRs comprise a large family of receptors, thus only those discussed in this review are shown above. Abbreviations: CARD (caspase recruitment domain), LRR (leucine rich repeat), BIR (baculovirus inhibition of apoptosis protein repeat), PYD (pyrin domain), FIIND (function to find domain), TIR (Toll-IL-1 receptor domain), helicase (DExD/H box helicase domain), CTD (carboxy terminal domain), HIN200 (hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear antigens with 200 amino acid repeats), L-L (di-leucine motif), 3aa (triad of acidic amino acids), Y (tyrosine-based motif), CRD (carbohydrate recognition domain), ITAM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif).