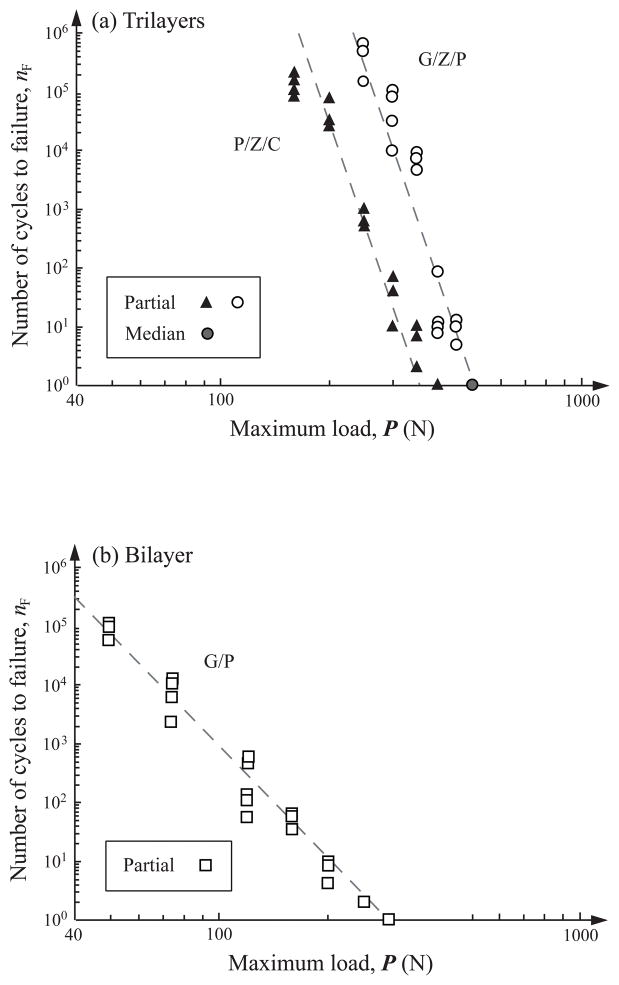
Fig. 4.
Plot of number of cycles nF to failure as a function of maximum load P for near-contact induced occlusal surface fractures in (a) porcelain/zirconia/composite (P/Z/C, solid triangles) and glass/zirconia/polycarbonate (G/Z/P, open and gray filled circles) trilayers and (b) glass/polycarbonate (G/P, open squares) bilayers following off-axis fatigue. In (a), the maximum fatigue loads P investigated are 160, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400 N for porcelain/zirconia/composite trilayers, and 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500 N for glass/zirconia/polycarbonate trilayers. Note in (a), median cracks (gray filled circle) are only observed at P = 500 N in glass/zirconia/polycarbonate trilayers. In (b), the maximum fatigue loads P used are 50, 75, 120, 160, 200, 250, 300 N for glass/polycarbonate bilayers. Indentation with tungsten carbide sphere of radius r = 1.5 mm, in water. Failure occurs when occlusal cracks (either partial cone or median cracks) penetrate to veneer/zirconia or glass/polycarbonate interfaces at critical number of cycles nF.