Fig. 10.
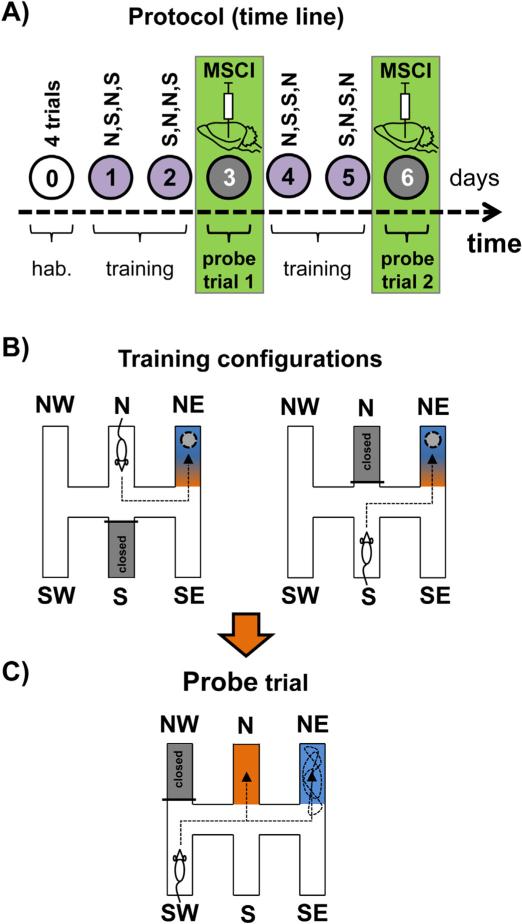
Analysis of strategy shifting capabilities in the double-H maze after reversible inactivation of the Re/Rh. (A) Time line of the experiment. After a habituation day (0), rats were trained for two consecutive days (1,2), given a first 24 h-delayed probe trial (3), trained for two additional days to strengthen learning (4,5) and given a second 24 h-delayed probe trial (6). On each training day they were released from the north (N) or south (S) arm according to the indicated sequence. Before each probe trial, rats were infused with muscimol (MSCI; 250 ng in 0.3 μL) or PBS. (B) Illustration of the configurations used during maze training. The rats were given 4 daily trials for which they were released twice from the S and twice from the N (in a randomized order; e.g., N,S,S,N, then S,N,N,S, then N,S,N,S. . .). The platform was always located in the NE arm. The arm opposite to the one in which the rats were placed at the start of a trial was always closed by a transparent guillotine door (it corresponds to the grey-filled arm). Rats could reach the target arm by one of both efficient response behavior (left-left or right-left turn sequences) or learn the place, and most probably, as shown earlier (Pol-Bodetto et al., 2011), made both in the place-response order. (C) On days 3 and 6, thirty min before each probe trial, about half the rats were infused with MSCI in the Re/Rh, the other half being infused with an equivalent volume of PBS as a control. For both probe trials, rats were released from the SW arm, the NW one was closed by a guillotine door; the platform had been removed from the device. We analyzed the capability of the rats to shift to a response based on place memory either immediately or after having entered the N arm. We found that in rats subjected to MSCI infusions into the Re/Rh such a shift was impossible, as also found in rats subjected to exactly the same protocol but given the infusions (250 ng in 1 μL) into either the mPFC or the hippocampus (Loureiro et al., unpublished data). This figure has been adapted from Cholvin et al. (2013).