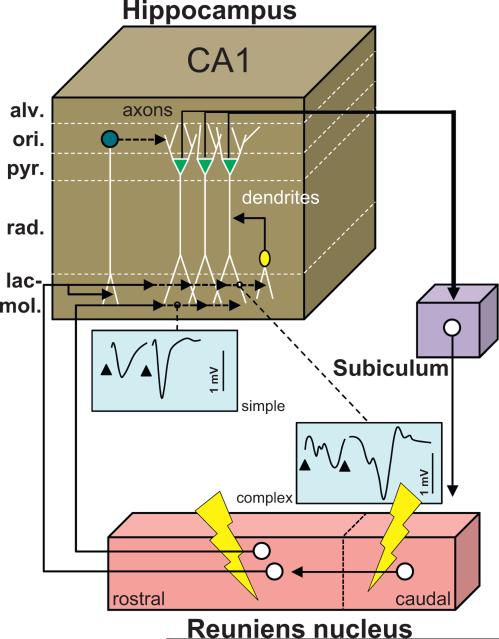
Fig. 5.
Functional scheme of the connectivity between the reuniens nucleus and the hippocampus. Drawing providing a summary of the main findings reported by Dolleman-van der Weel et al. (1997) and hence derived connectivity loop which they proposed. Neurons from the caudal region of the Re project to the rostral Re, from where neurons establish monosynaptic contacts with the dendrites of pyramidal CA1 cells in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare, of interneurons with their soma in the stratum radiatum, and of interneurons with their soma in the stratum oriens. Most contacts in this model are excitatory, except the contacts of the interneurons of the stratum oriens which mediate feedforward inhibition on CA1 pyramidal neurons. The axons of the latter, which course in the alveus, project back to the Re via the subiculum. A stimulation of the Re using a paired stimulation protocol will produce facilitation and exhibit two types of evoked activity profiles in the stratum lacunosum-moleculare depicted as simple (one negative deflection/stimulation) and complex (2 deflections/stimulation). The complex profiles are obtained with caudal stimulation of Re and most probably correspond to the disynaptic EPSPs. This figure has been drawn after Fig. 6 in Dolleman-van der Weel et al. (1997). Abbreviations: alv: alveus; lac-mol: stratum lacunosum-moleculare; ori: stratum oriens; pyr: stratum pyramidale; rad: stratum radiatum.