Figure 8.
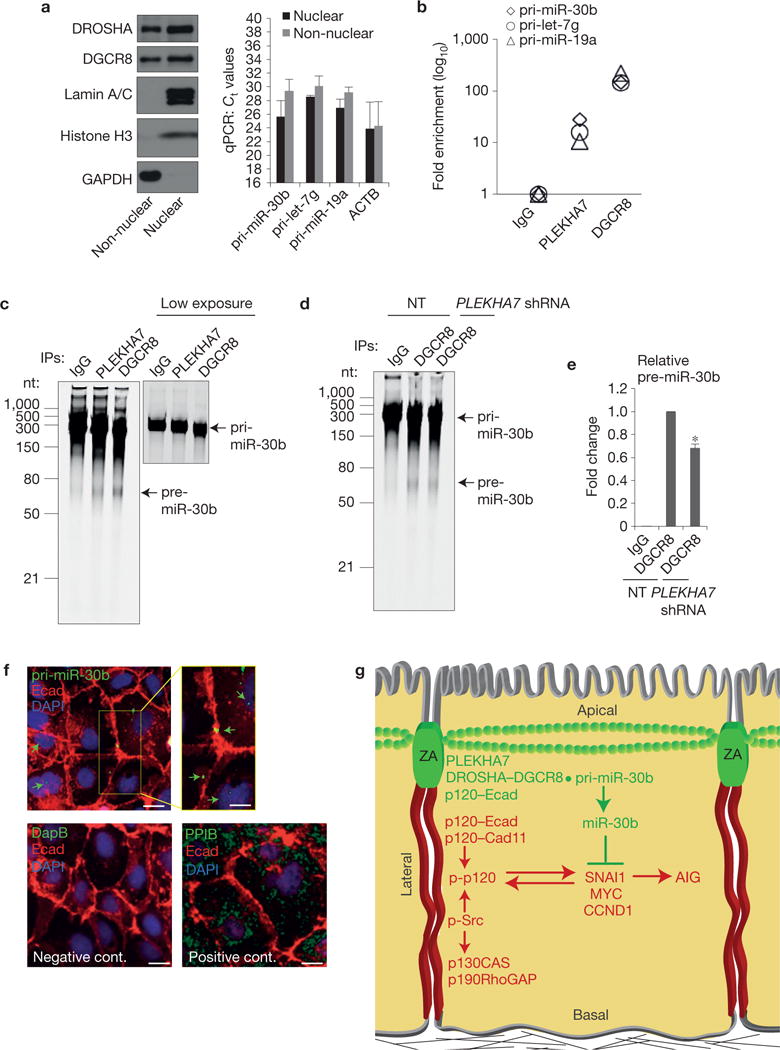
PLEKHA7 regulates pri-miR-30b processing at the junctions. (a) qRT–PCR of isolated nuclear and non-nuclear subcellular fractions of Caco2 cells for the indicated pri-miRNAs (right panel). Successful fractionation is demonstrated by western blot for the indicated markers (left panel). Ct values are shown (mean ± s.d. from n = 3 independent experiments); actin (ACTB) is the positive qRT–PCR control. Lamin A/C and histone H3 are the nuclear and GAPDH the cytoplasmic markers for the western blot. See Supplementary Fig. 8 for unprocessed blot scans. (b) qRT– PCR of the eluates from the IgG (negative control), PLEKHA7 and DGCR8 (positive control) RNA-IPs for the indicated pri-miRNAs (a representative is shown from two independent experiments). (c) In vitro pri-miR-30b processing activity assay of Caco2 lysates for PLEKHA7, DGCR8 (positive control) and IgG (negative control) IPs. A lower exposure image of the pri-miR-30b template is presented to show the actual loading amount. nt, nucleotides. (d) In vitro pri-miR-30b processing activity assay for DGCR8 IPs of NT or PLEKHA7 shRNA Caco2 cells; IgG is the negative control. (e) Quantification of pre-miR-30b band intensities from n =3 independent in vitro processing activity assays, carried out as in d (mean ± s.d.; *P <0.001, Student’s two-tailed t -test). (f) ISH of Caco2 cells for pri-miR-30b; a bacterial DapB RNA probe was used as the negative and the endoplasmic-reticulum-specific PPIB as the positive control. Merged images are shown. An enlarged area in the yellow box in the top right panel is shown for the pri-miR-30b ISH. Arrows indicate hybridization signals. Scale bars for full images, 20 μm; for enlarged part, 12 μm. Source data are provided in Supplementary Table 2 for a,b and e. (g) Schematic diagram summarizing the findings of the present study. Two distinct junctional complexes exist in polarized epithelial cells: a basolateral complex lacking PLEKHA7 promotes growth signalling and anchorage-independent growth (AIG) through cadherins, Src and p120 activity, whereas an apical ZA complex suppresses these events through PLEKHA7, by locally recruiting the microprocessor at the ZA to regulate processing of miR-30b.
