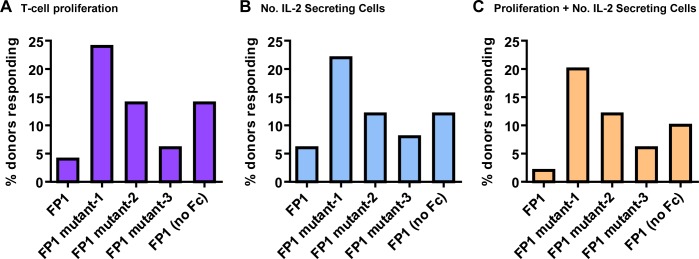
Fig 2. Biotherapeutics with minor differences in sequence can be distinguished by the IVCIA assay.
Several sequence variants of FP1 varying by one (mutant-1 and mutant-2) or two (mutant-3) amino acids, as well as FP1 lacking the Fc domain (FP1 (no Fc)) were tested in the in the IVCIA assay using 50 healthy human donors over 5–8 days. FP1 is a biotherapeutic fusion protein of an enzyme fused to the Fc domain of a monoclonal antibody. The percentage of donors with either A) a positive T-cell proliferative response ([3H]-thymidine uptake) or B) an increase in the number (No.) of IL-2 secreting cells (Elispot), or C) both positive T-cell proliferative responses and an increase in the number of IL-2 secreting cells are shown. A response was considered positive if the SI≥2.0 (p<0.05) above the background response.