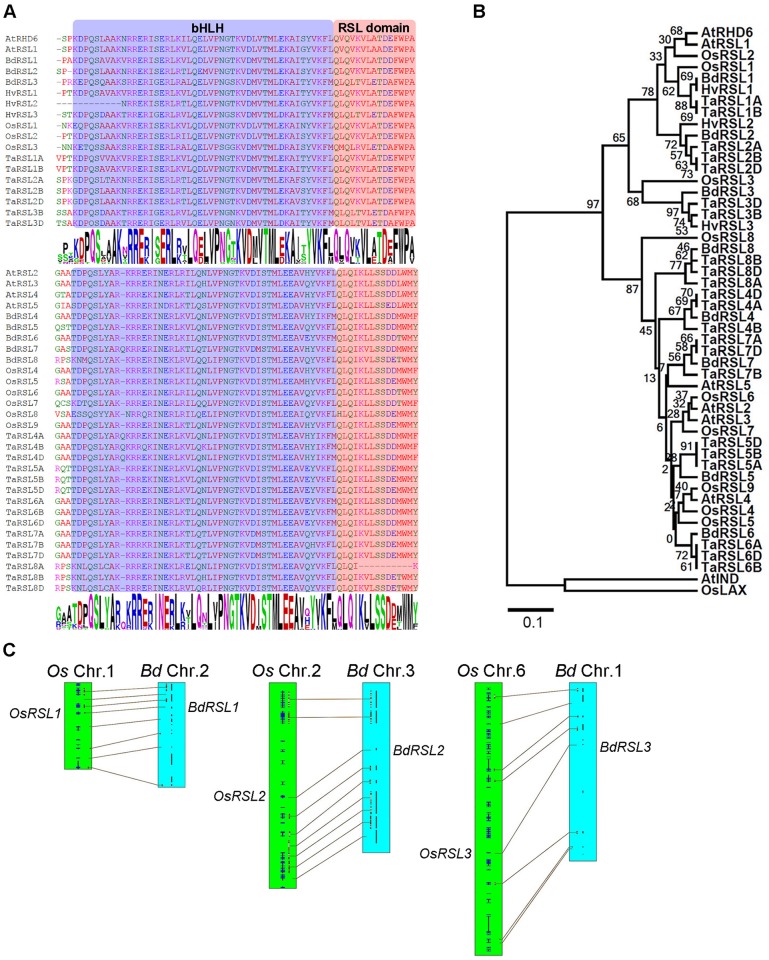
Fig 1. Genes encoding RSL class I proteins are present in the genomes of members of the grass family.
(A) Alignment of conserved regions of Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), Oryza sativa (Os), Triticum aestivum (Ta), Hordeum vulgare (Hv) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At) RSL class I proteins. The position of the bHLH and RSL domains is indicated by coloured boxes shaded blue and red respectively. The sequence logos represent the multiple alignment of RSL class I and class II amino acid sequences from five plant species (S1A Fig); heights are proportional to amino acid conservation in each position. (B) Maximum-likelihood tree showing the relationship between RSL class I and class II proteins from Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), Oryza sativa (Os), Triticum aestivum (Ta), Hordeum vulgare (Hv) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At) based on the protein sequence of bHLH and RSL domains. AtbHLH040 (AtIND) and OsbHLH123 (OsLAX) were used as out groups. Numbers below branches indicate bootstrap percentages. (C) Synteny between RSL class I genes of B. distachyon and O. sativa. Connecting lines between linkage groups define chromosome regions with collinear orthologous genes. The locations of RSL1, RSL2 and RSL3 orthlogs are indicated.