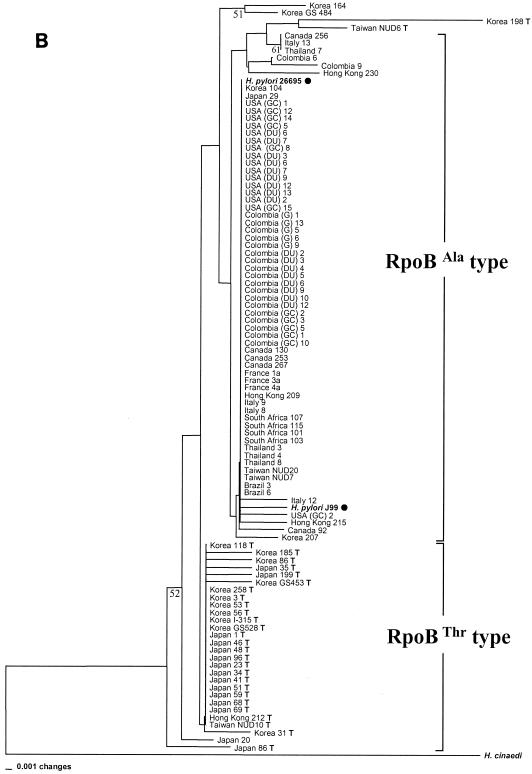
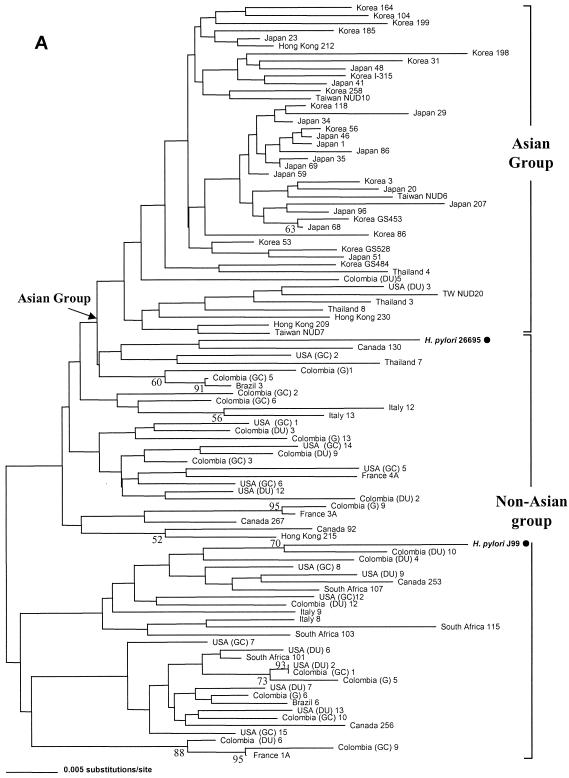
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of 100 H. pylori isolates inferred from partial rpoB DNA sequences (A) and RpoB amino acid sequences (B). The H. pylori population was separated into an Asian group, to which most of the Asian strains belonged, and a non-Asian group, which was mainly composed of Western strains (North and South American, European, and South African strains), including strains H. pylori 26695 and H. pylori J99, by nucleotide sequence analysis (A). Two large groups (RpoBAla and RpoBThr) in the amino acid tree (B) were attributed to the identity of the 497th residue of each strain, which is either alanine or threonine. RpoBThr strains have the suffix T. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method in the PAUP package. The bootstrap values presented at the corresponding branches were evaluated from 1,000 replications, and values less than 50% are not indicated.