Figure 1.
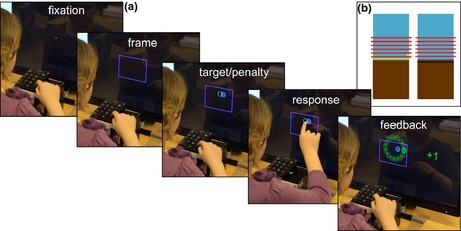
(A) A 9‐year‐old girl demonstrates a typical trial sequence. The blue penalty circle in the example has a gain of −1, and a 1.5 × radius offset from target centre (‘far 1' condition). (B) The current total score (which could be negative) was displayed graphically throughout the session. The brown area is ‘the ground’, the blue area ‘the sky’. For each point gained, a coin appeared (left example). For each point lost, a coin was removed. For every 20 coins (denoted by a red line), subjects won a token that could be exchanged for toys (or £0.50 for adults) at the end. If the total score became negative, each lost point would create a ‘hole’ in the ground (right example). Before getting back into the sky, coins had to be won to fill up the holes.
