Fig. 3.
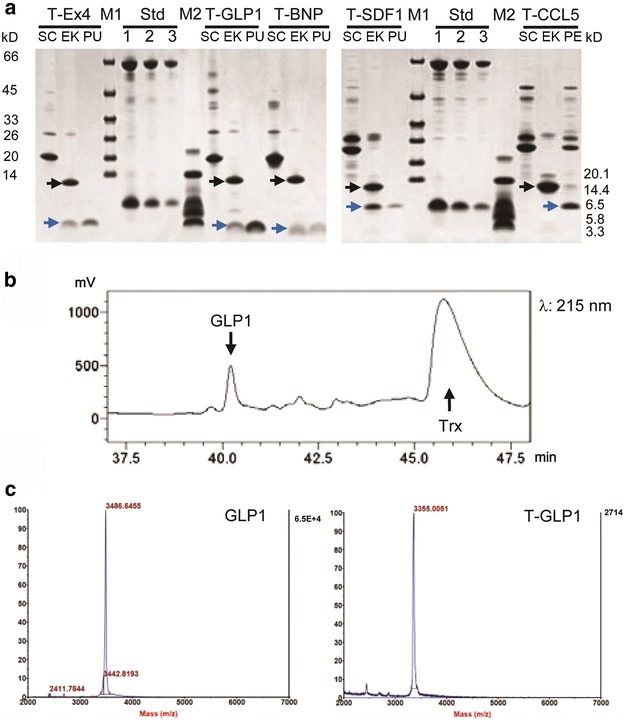
Production of target peptides with native N-terminus by removal of the Trx tag. a Enterokinase cleavage of Trx-peptide and purification results for different target peptides, designated with T-Ex4, T-GLP1, T-BNP, T-SDF1, and T-CCL5. Black arrow Trx; blue arrow target peptide. Lanes SC and EK, Trx-peptide before (soluble fraction of intein cleaved fusion protein) and after enterokinase cleavage; lane PE, precipitate after enterokinase cleavage of T-CCL5; lane PU, final product of target peptide after RP-HPLC purification; lanes 1, 2, and 3, quantification standards (Std) consisting of bovine serum albumin (BSA, 66.5 kDa) at 3, 1.5, and 0.75 µg/lane and aprotinin (6.5 kDa) at 1.5, 0.75, and 0.3 µg/lane, respectively. The molecular masses of the protein standards M1 and M2 are listed by the left and right side separately. b RP-HPLC separation of target peptide and Trx after enterokinase cleavage, illustrated by the chromatographic diagram of GLP-1. X axis retention time; Y axis peak height measured in mV. c MALDI-TOF analysis of GLP-1 produced using the vector pET-P-Intein-ELK16 (GLP1, left) or pET-Trx-P-Intein-ELK16 (T-GLP1, right)
