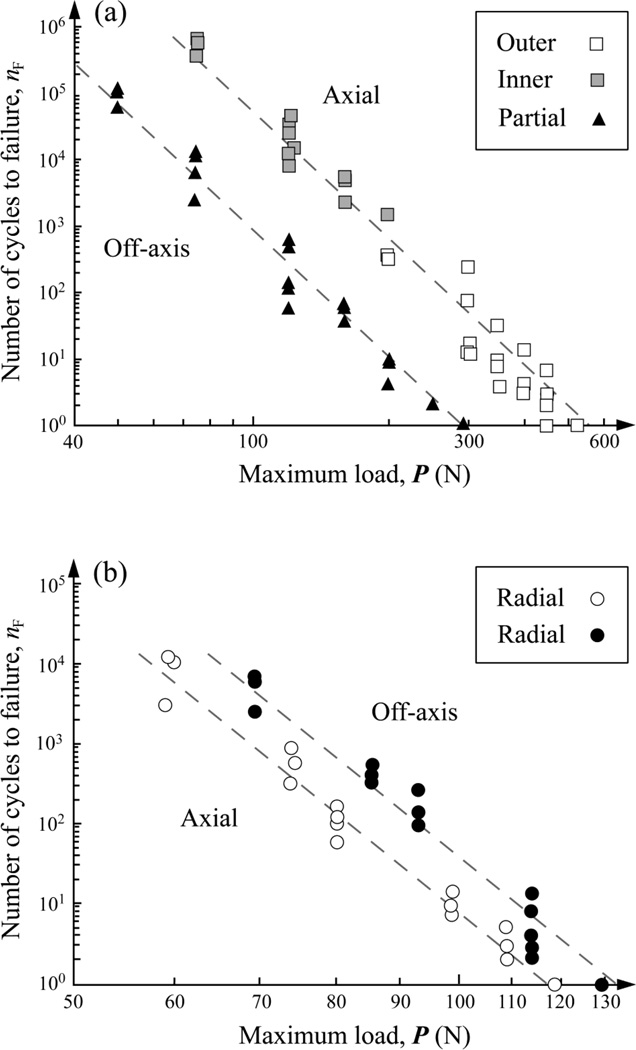
Fig. 4.
Plot of number of cycles nF to failure as a function of maximum load P in glass/polycarbonate bilayers for (a) occlusal surface cone fracture and (b) cementation surface radial fracture following axial and off-axis fatigue. In (a), the maximum fatigue loads P investigated were 75, 120, 160, 200, 300, 350, 400, 450, and 510 N for axial loading, and 50, 75, 120, 160, 200, 250, and 290 N for off-axis loading. In (b), the maximum fatigue loads P used are 60, 75, 80, 99, 109, and 119 N for axial loading and 69, 86, 93, 114, and 129 N for off-axis loading. Indentation with tungsten carbide sphere of radius r = 1.5 mm, in water. Failure occurs when occlusal cone cracks penetrate to glass/polycarbonate interface or cementation radial cracks pop-in at critical number of cycles nF.