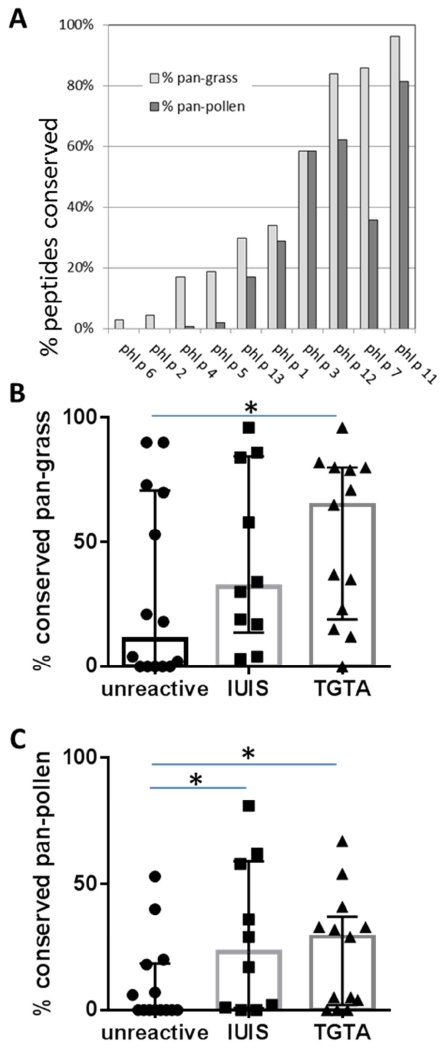
Figure 1. Conservation of TG proteins across other pollens.
(A) 648 peptides from IgE reactive Phl p allergens listed by IUIS were examined for their conservation in other pollen species. Peptides were considered conserved in another pollen if its transcriptome encoded the peptide or a variant with up to 2 amino acid substitutions. The percentage of peptides conserved in all 4 additional grass transcriptomes (‘pan-grass’) is indicated in light grey bars, and the percentage of peptides conserved in all ten pollens (‘pan-pollen’) in dark grey bars. Antigens are sorted based on pan-grass conservation from low to high. The pan-grass (panel B) and pan-pollen (panel C) conservation of IUIS allergens was then compared to proteins identified in Phl p pollen based on a transcriptomic and proteomic analysis. Median and quantile ranges are indicated by boxes and error bars. Phl p pollen proteins that were not recognized by either T-cell or B cell responses were less conserved than both IUIS allergens and Timothy Grass T-cell antigens (TGTAs). Asterisks indicated statistically significant differences (one-tailed Mann-Whitney test, p < 0.05).