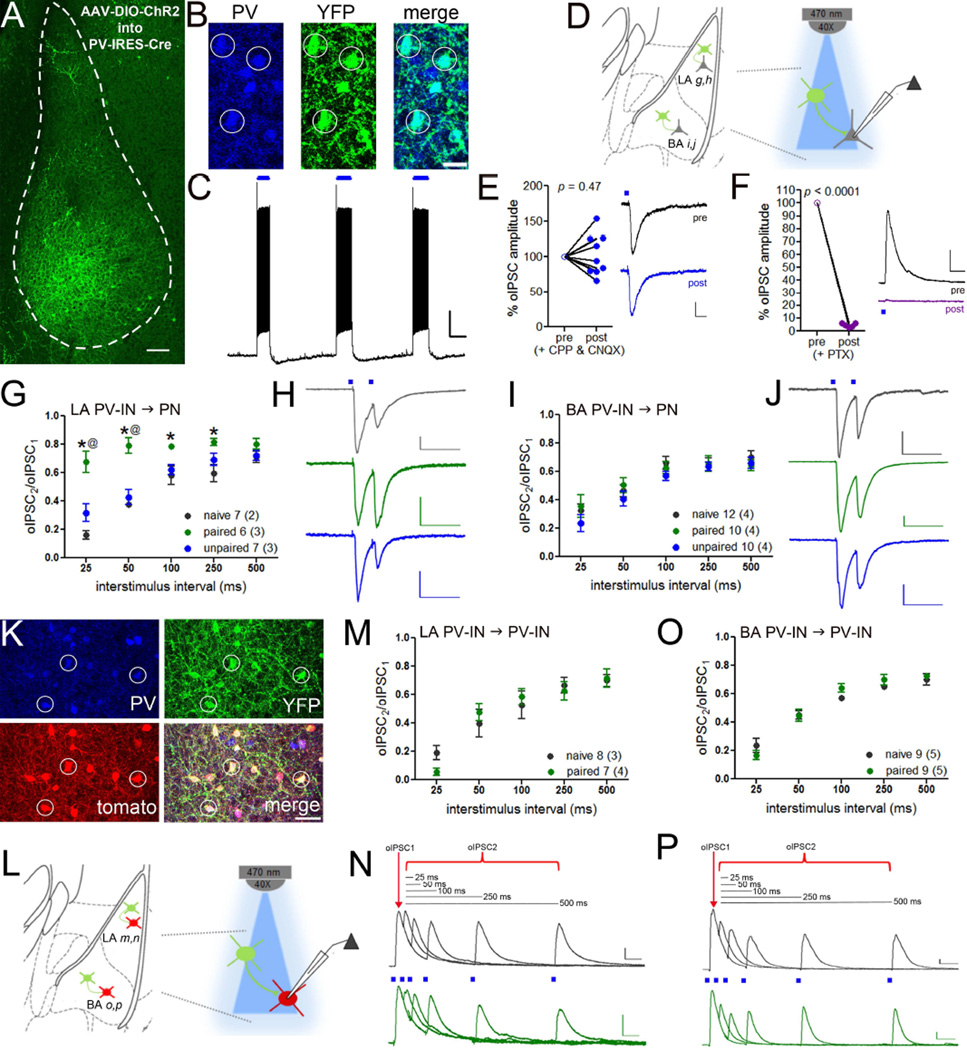
Figure 6. Nucleus- and target-specific reduction in GABA release from PV-INs after auditory fear conditioning.
A. AAV-DIO-ChR2-eYFP was injected into the basolateral amygdala of PV-IRES-Cre mice for optogenetic-assisted in vitro slice electrophysiology, scale = 100 µm. B. Immunofluorescence staining confirmed that eYFP (green) was exclusively expressed in PV-positive neurons (blue), scale = 25 µm. C. Blue light (λ= 470 nm) evoked action potential generation in ChR2+ PV-INs. Scale = 15 mV × 1 s. D. Recording configuration in E–H. Release probability at PV-IN → principal neuron (PN) synapses was assayed by paired-pulse optic stimulation (λ= 470 nm) in LA (G–H) and BA (I–J). D–E. Light-evoked currents were unaffected by the glutamate receptor antagonists APV and CNQX (E, scale = 20 pA × 25 ms) and abolished by PTX (F, scale = 100 pA × 50 ms). G. Paired pulse ratio (PPR) of PV-IN → PN IPSCs in LA was increased in mice that received paired training compared to unpaired and naïve conditions. Representative traces in H. I. PPRs were unaltered in BA. Representative traces in J. Representative traces are shown at the 50 ms interstimulus interval. Scales = H, 50 pA × 100 ms; J, 60 pA × 100 ms. K. AAV-DIO-ChR2-eYFP was injected into the basolateral amygdala of PV-IRES-Cre mice crossed to ROSA-tdTomato reporter mice to target PV-INs for electrophysiological recordings without gating ChR2. L. Schematic of O–R. Release probability at PV-IN → PV-IN synapses was assayed by paired-pulse optical stimulation (λ = 470 nm) during recording from tdTomato-positive PV-INs in LA (M–N) and BA (O–P). M–P. PPR of PV-IN → PV-IN IPSCs was unaffected by training in the LA (M, representative traces in N) and BA (O, representative traces in P). IPSC recordings were conducted at 0 mV in order to exclude postsynaptic ChR2 currents based on their ionic reversal. Scales = N,P 50 pA × 50 ms. n/group indicated on graphs. E,F paired samples t-test; G,I,M,O repeated measured ANOVA followed by planned comparisons with Holm-Bonferroni. * p < 0.05 naïve versus paired, @ p < 0.05 paired versus unpaired. Data presented as mean ± SEM.