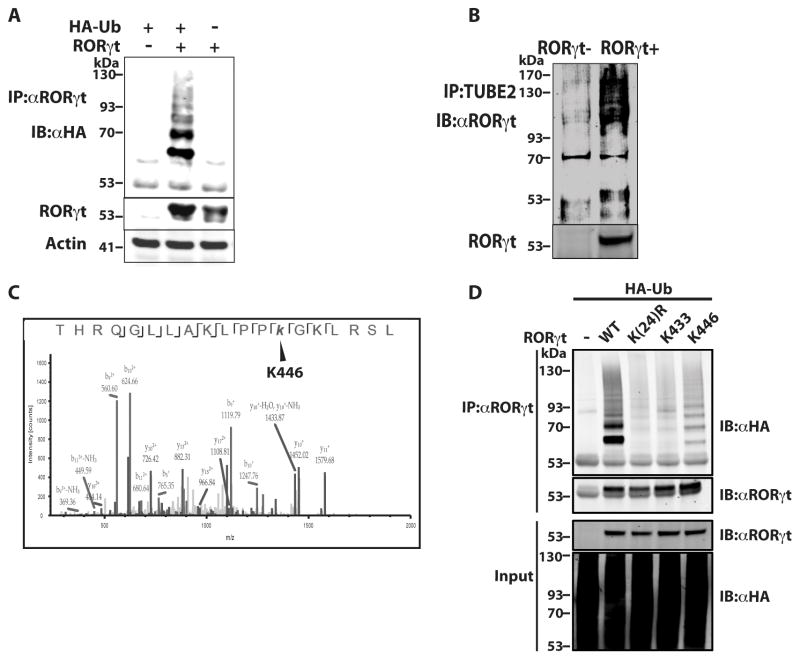
Figure 1.
K446 of RORγt is a ubiquitination site. (A) Expression plasmids encoding RORγt and HA-Ub were transfected into 293T cells for 48 h. RORγt was then immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-RORγt antibody (αRORγt) and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Ubiquitinated RORγt was detected by immunoblot (IB) with anti-HA antibody (αHA). Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Purified naïve CD4+ T cells were differentiated under Th17 priming conditions (TGFβ and IL-6) for three days. Ubiquitinated proteins in the purified cell lysates were enriched by IP with TUBE beads and resolved on an SDS-PAGE gel. RORγt in the immunoprecipitated ubiquitinated proteins was then detected by IB with anti-RORγt antibody. (C) RORγt immunoprecipitated from differentiated Th17 cells was digested by trypsin and analyzed by MS. Shown are the MS/MS peptide spectra that identified K446 as a ubiquitination site. (D) Expression plasmids encoding RORγt or indicated RORγt mutants and HA-Ub were transfected into 293T cells for 48 h. RORγt was then IP with αRORγt and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Ubiquitinated RORγt was detected by IB with αHA. Data shown except (C) are the representatives of at least three independent experiments.