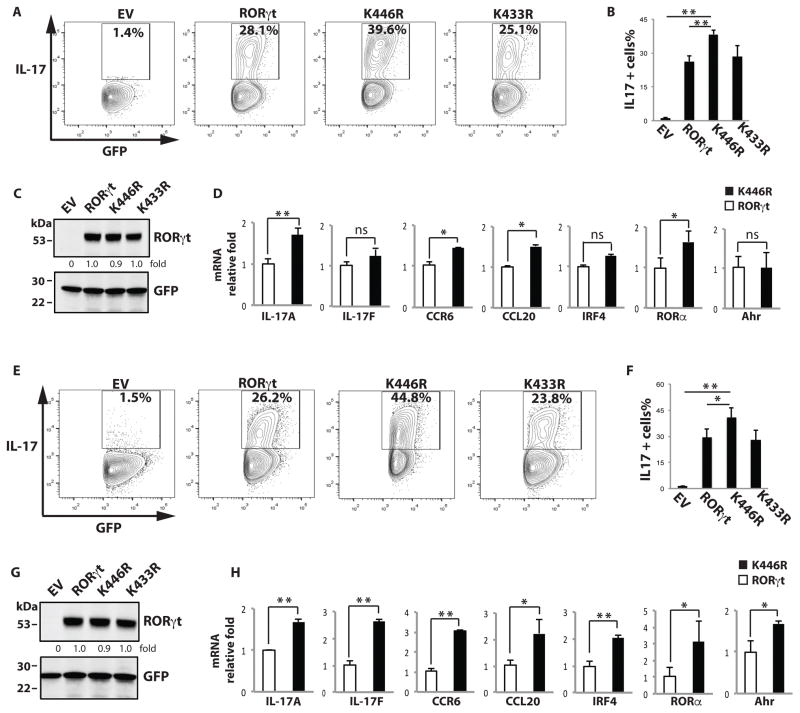
Figure 2.
K446 ubiquitination negatively regulates Th17 differentiation. (A–C) T cells obtained from RORγt/− mice were transduced with retrovirus expressing GFP only (empty virus, EV) or together with RORγt WT, K446R, or K433R, and differentiated under Th17-differentiating conditions. Three days later, intracellular IL-17 was detected by flow cytometry. Percentages of IL-17+ cells among GFP+ cells are indicated. B is the summary of three independent experiments. RORγt and GFP expression was detected by westernblot analysis in C, and expression levels relative to wild type RORγt was calculated. (D) RNA was prepared from RORγt (open bars)- or K446R (black bars)-reconstituted RORγt−/− T cells differentiated under Th17 conditions. qPCR was performed to quantitate expression of the indicated genes. * P < 0.05, ** P<0.01. ns stands for not significant. (E–G) Differentiated Th17 cells described in (A) were rested in IL-2 for 48 h, placed in Th17 differentiation conditions for 3 more days, and analyzed as described in (A). F is the summary of three independent experiments. RORγt and GFP expression was detected by westernblot analysis in G, and expression levels relative to wild type RORγt was calculated. (H) Critical Th17 gene expression in RORγt (open bars)- or K446R (black bars)-reconstituted RORγt−/− T cells rested and redifferentiated as described in (E) was analyzed by qPCR. Unless specified, data shown are the representative of at least three independent experiments.