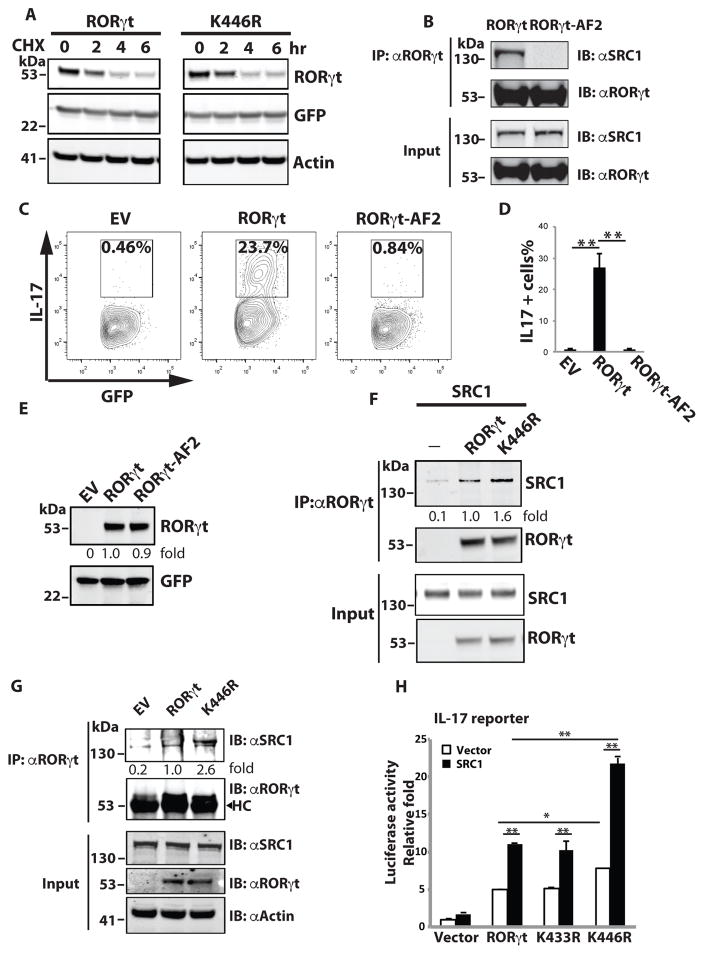
Figure 3.
K446 ubiquitination impairs RORγt activity by reducing the recruitment of co-activator SRC1. (A) Expression plasmids for GFP together with RORγt or K446R were transfected into 293T cells for 48 h. Cells were then treated with protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated time (hr) and RORγt and GFP were detected by IB. (B) RORγt WT or AF2 mutant was expressed with SRC1 in 293T cells for 48 h. IP was performed to detect RORγt-SRC1 interactions. (C–E) RORγt−/− T cells were transduced with retrovirus expressing GFP only (empty virus, EV) or together with RORγt WT or AF2 mutant, and differentiated under Th17 conditions. Three days later, intracellular IL-17 was detected by flow cytometry. Percentages of IL-17 positive cells among GFP+ cells are indicated. D is the summary of three independent experiments. RORγt and GFP expression was detected by westernblot analysis in E. (F) RORγt WT or K446R was expressed with SRC1 in 293T cells for 48 h. IP was performed to detect RORγt-SRC1 interactions. Immunoprecipitated SRC1 levels relative to that immunoprecipiated by wild type RORγt was calculated. (G) RORγt WT or K446R was transduced into RORγt−/− T cells differentiated under Th17 conditions for three days. IP was performed to detect RORγt-SRC1 interactions. Immunoprecipitated SRC1 levels relative to that immunoprecipiated by wild type RORγt was calculated. HC indicates heavy chain. (H) IL-17 promoter luciferase reporter was transfected into 293T cells with control or SRC1 plasmid and indicated RORγt mutants for 24 h. Luciferase assay was performed to quantitate relative reporter activity. Data represent mean ± SE from three independent experiments with at least two replicas in each experiment. *<0.05 and **<0.01. Unless specified, data shown are the representative of at least three independent experiments.