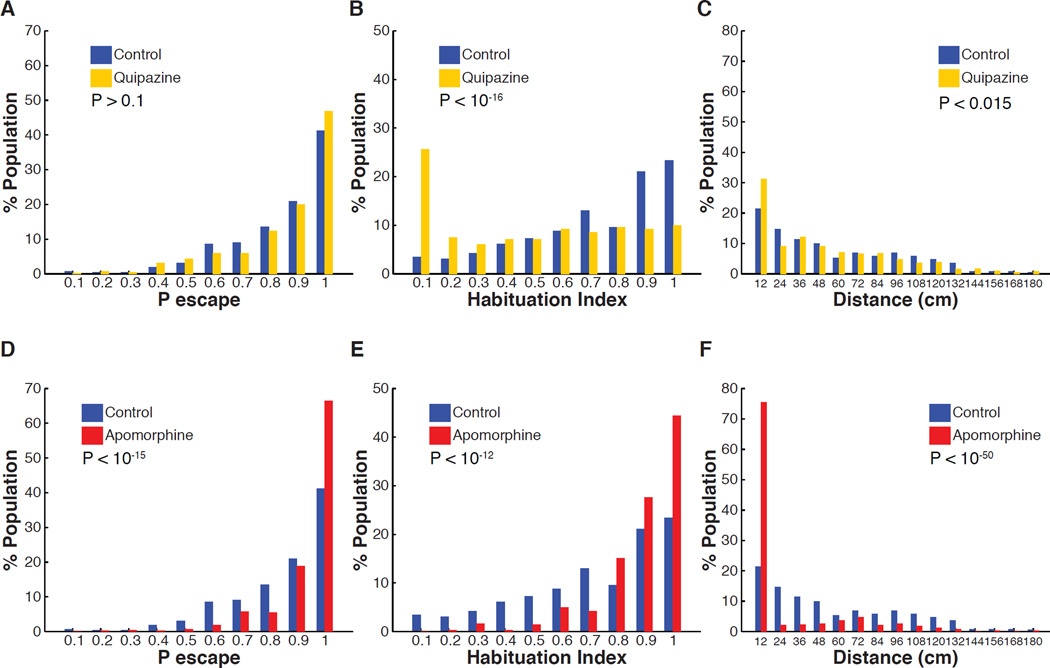
Figure 5. Effect of serotonin and dopamine agonists on ASR habituation and spontaneous swim behavior.
(A–C) Treatment with serotonin receptor agonist (quipazine 50 µM). (A) Quipazine treatment does not significantly affect ASR probability under non-habituating conditions (nControl = 420, nQuipazine = 420, z = 1.53, P > 0.1). (B) Quipazine treatment shifts the habituation index (HI) frequency distribution to lower values (less habituation) (nControl = 261, nQuipazine = 281, z = 8.4, P < 10−16). (C) Quipazine treatment shifts the frequency distribution of total displacement during 10 minutes to lower values when compared to control group (nControl = 359, nQuipazine = 394, z = 2.5 P < 0.015). (D–F) Treatment with dopamine receptor agonist (apomorphine 15 µM). (D) Apomorphine treatment increases initial ASR probability (nControl = 420, nApomorphine = 420, z = 8.2, P < 10−15). (E) Apomorphine treatment shifts HI frequency distribution to higher values (greater habituation) (nControl = 261, nApomorphine = 358, z = 7.38, P < 10−12). (F) Apomorphine treatment significantly shifts the frequency distribution of total displacement values during 10 minutes to lower values when compared to control group (nControl = 359, napomorphine = 383, z = 15.12, P < 10−50).