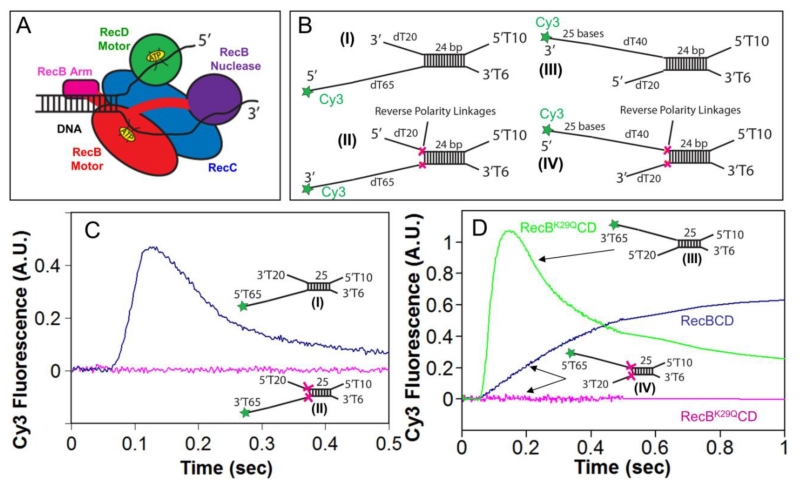
Figure 1. Reversal of the sugar-phosphate backbone polarity prevents ssDNA translocation of the RecB and RecD canonical motors.
A. Cartoon of RecBCD bound to a dsDNA end based on a crystal structure[3]. RecB, RecC, and RecD are shown in red, blue, and green, respectively, with the RecB arm and nuclease domains shown in pink and purple.
B. DNA substrates used to test the effects of reverse polarity (RP) linkages on ssDNA translocation. The red X indicates the positions of the 3′-3′ and 5′-5′ RP linkages. A green star indicates the position of a Cy3 fluorophore.
C. Stopped-flow time courses monitoring Cy3 fluorescence were obtained by pre-incubating RecBCD (18.75 nM) with DNA I (blue trace) or DNA II (red trace) (25 nM) in Buffer M (250 mM NaCl) with ATP (1 mM) and heparin (8 mg/mL) in buffer M (8 mM NaCl) at 1:10 volumetric ratio yielding a final NaCl concentration of 30 mM (concentrations of RecBCD and DNA listed are after mixing) at 25° C.
D. Stopped-flow time courses monitoring Cy3 fluorescence performed as described for panel C. RecBK29QCD pre-incubated with DNA III (green trace) or DNA IV (red trace); RecBCD pre-incubated with DNA IV (blue trace).