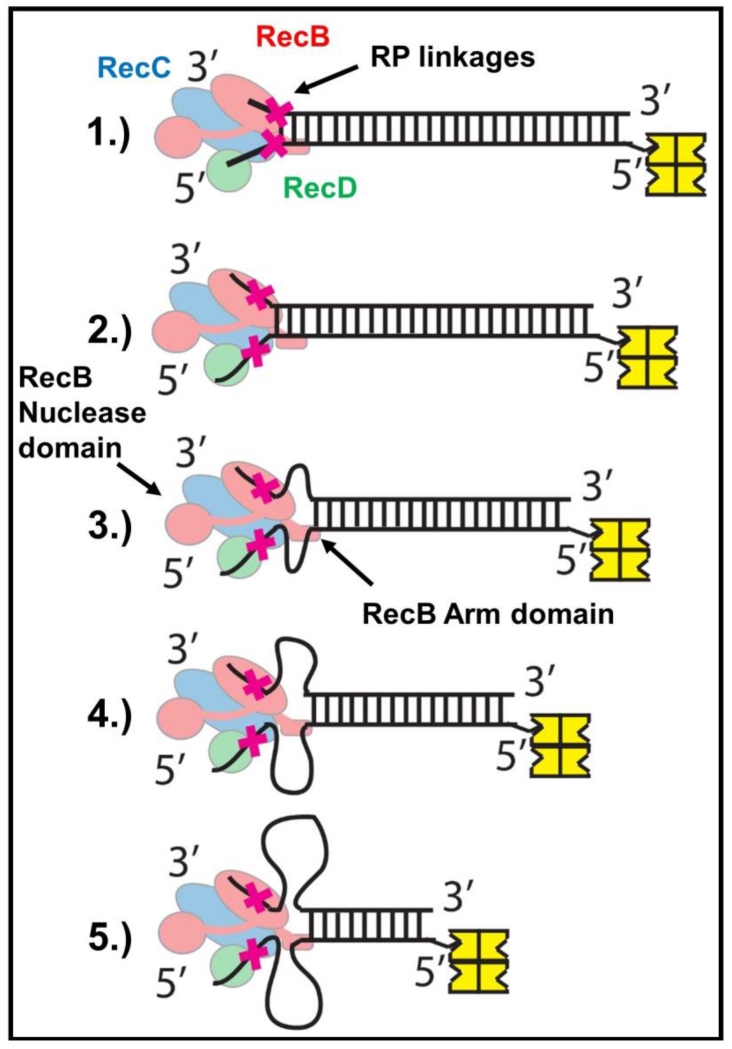
Figure 7. Proposed mechanism for unwinding of reversed polarity DNA by RecBCD.
(Step 1) RecBCD binds to and melts 6 base pairs at a normal DNA end. (Step 2) Canonical ssDNA motors (RecB (red) and RecD (green)) translocate along the ssDNA tracks until the RP linkages (red X) are encountered. (Step 3-5) RP linkages block ssDNA translocation by the canonical RecB and RecD motors, but the secondary translocase, fueled by ATP hydrolysis in the RecB motor, simultaneously pulls dsDNA toward RecBCD, resulting in the formation of single stranded DNA loops. The RecB Arm and RecB Nuclease domains (highlighted) are necessary for this activity.