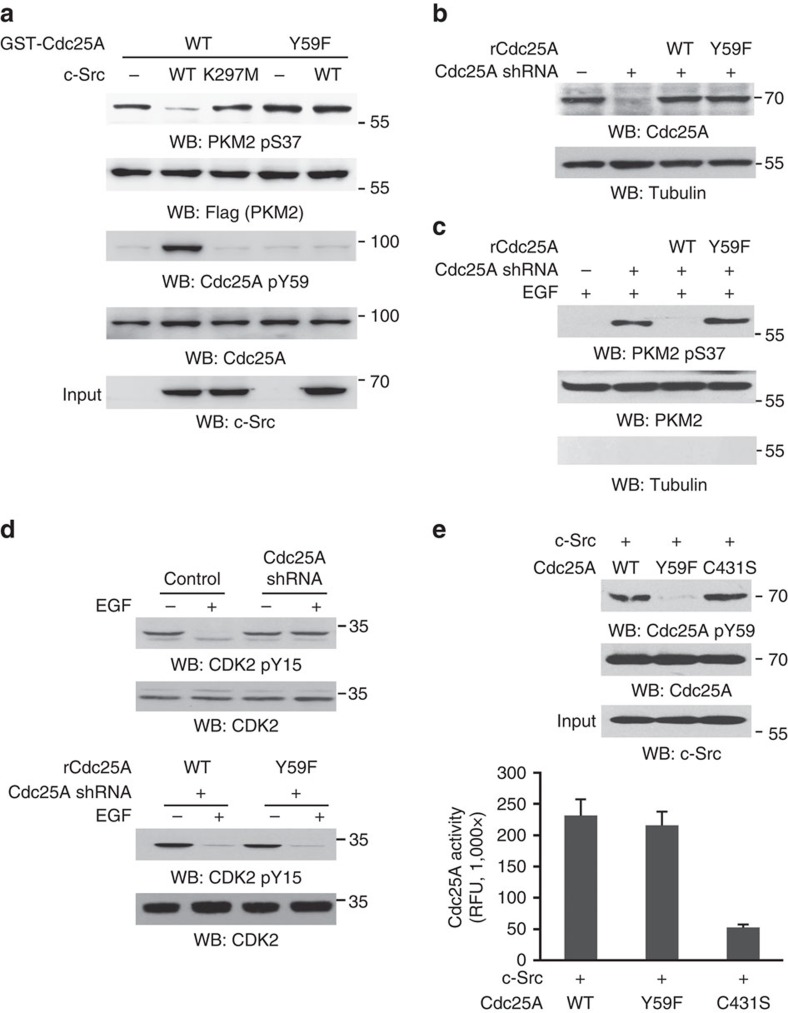
Figure 3. c-Src-phosphorylated Cdc25A Y59 dephosphorylates nuclear PKM2 pS37.
Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (a) Flag-PKM2, which was phosphorylated at Ser 37 by EGF treatment (100 ng ml−1) for 3 h in U87/EGFR, was immunoprecipitated and eluted by Flag peptides. Immobilized and purified WT GST-Cdc25A or GST-Cdc25A Y59F was mixed with or without wild-type c-Src or kinase-dead c-Src K297M for an in vitro kinase assay. After the reaction, GST-Cdc25A was pulled down and incubated with eluted Flag-PKM2 in a phosphatase buffer for dephosphorylation reaction. (b,c) Endogenous Cdc25A-depleted U87/EGFR cells were reconstituted with the expression of rCdc25A WT or rCdc25A Y59F (b). These cells were treated with EGF (100 ng ml−1) for 6 h. Nuclear fractions of the cells were extracted (c). (d) U87/EGFR cells with depleted Cdc25A and reconstituted the expression of rCdc25A WT or rCdc25A Y59F were treated with or without EGF (100 ng ml−1) for 30 min. (e) An in vitro kinase assay was performed by mixing Cdc25A WT, Y59F mutant or C431S mutant with active c-Src. After the reaction, immunoblotting analyses were performed with the reaction mixture (upper panel), or GST-Cdc25A WT and mutants were pulled down by glutathione agarose beads, and their activities toward FDP were examined using an Enzolyte FDP Protein Phosphatase Assay Kit (lower panel). Data represent the mean±s.d. of three independent experiments.