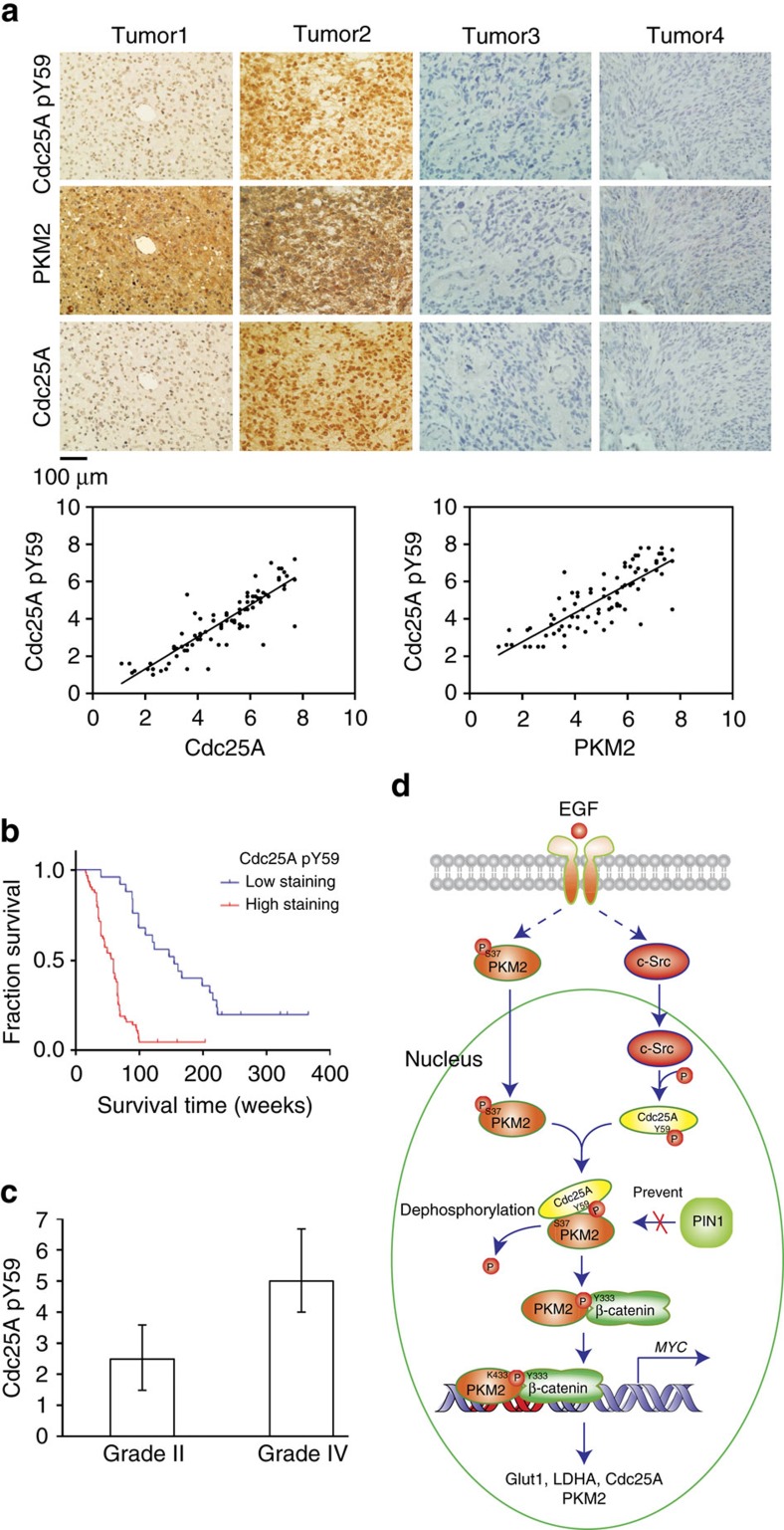
Figure 7. Cdc25A pY59 levels positively correlate with PKM2 and Cdc25A protein levels in human GBM samples and indicate prognosis.
(a) Immunohistochemical staining of 88 GBM specimens with anti-phospho-Cdc25A-Y59, anti-PKM2 and anti-Cdc25A antibodies was performed. Top panel, representative photographs of four GBM specimens; bottom panel, semi-quantitative scoring (using a scale from 0 to 8) was carried out (Pearson product moment correlation test, left panel, r=0.88, P<0.001; right panel, r=0.82, P<0.001). (b) The survival times for 88 patients with low (0–4 staining scores, blue curve) versus high (4.1–8 staining scores, red curve) Cdc25A Y59 phosphorylation (low, 24 patients; high, 64 patients) were compared. Landmark represents censored (alive at last clinical follow-up) patients. (c) Thirty diffuse astrocytoma specimens were immunohistochemically stained with anti-phospho-Cdc25A-Y59 antibody, and specimens were compared with 88 stained GBM specimens (Student's t test, two-tailed, P<0.001). Data represent the mean±s.d. of 30 astrocytoma specimens and 88 GBM specimens. (d) A mechanism of Cdc25A-promoted Warburg effect and tumorigenesis. EGFR activation results in c-Src-dependent phosphorylation of Cdc25A at Y59. Phosphorylated Cdc25A binds to and dephosphorylates PKM2 pS37. PKM2 pS37 dephosphorylation is required for PKM2- and β-catenin-dependent c-Myc expression, which in turn promotes expression of glycolytic genes and Cdc25A, the Warburg effect and tumorigenesis.