Table 1. Comparison of crosstalk levels between the different variants of the model.
| Model | Crosstalk (at baseline parameters) | Remarks |
| Basic model (activators-only) | 0.23 | |
| Basic model (repressors-only) | 0.23 | |
| Mixed model (activators+repressors) | 0.14 | 2,000 genes expressed in 20% of the env., 3,000 genes in 70% |
| Genes of unequal importance | 0.31 | 10% of the genes are important and penalized 10 × the ‘normal' rate |
| The resulting error per important gene decreases to 0.1, but for the other genes increases to 0.33. | ||
| Unequal weights for the two error types | 0.17 | b=0.5, weight of erroneously active genes is half that of genes that are erroneously inactive |
| Each TF regulates exactly Θ=10 genes | 0.08 | Also holds for P(Θ)∼Poisson 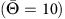
|
| Activators+global nonspecific repressor | 0.23 | Cannot reduce crosstalk |
| Activators+specific repressors (non-overlapping) | 0.2 | |
| Activators+specific repressors (overlapping) | 0.15 | |
| Perfect AND-gate combinatorial regulation | 0.07 | Uses only 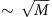 TF species TF species |
| Generic cooperativity | 0.064 | For example, dimerization, direct TF–TF contacts, TF/nucleosome competition and so on. Two bindings sites, each of length L=10 |
| Cooperativity exclusive to cognate binding | 0.006 | Currently unknown molecular mechanisms, two bindings sites, each of length L=10. |
Baseline parameters are: Q=2,500, M=5,000, log(S)=−10.5—equivalent to a model where binding sites for distinct TFs are different from each other in at least 2 bp (dmin=2) with binding sites of L=10 bp and binding energy 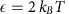 per mismatch.
per mismatch.
