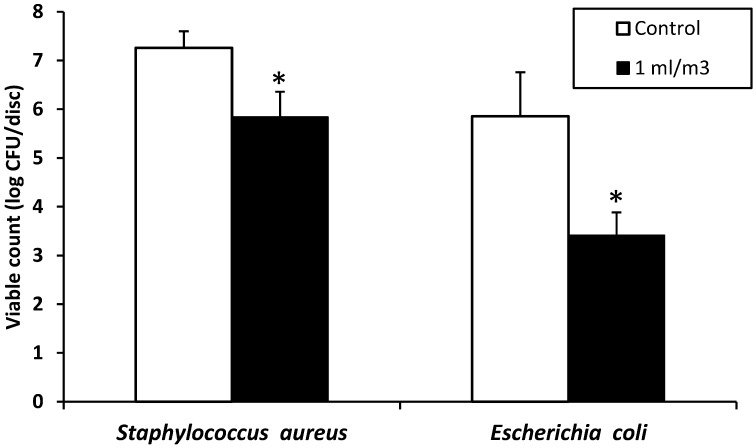
Fig. 4.
Antibacterial effects of ClO2 gas on S. aureus and E. coli without using an electric humidifier. The relative humidity in the test room was 30% to 40%. ClO2 gas was generated by mixing 3.35% sodium chlorite solution and 85% phosphoric acid at a 10:1 volume ratio. Sodium chlorite solution was used at a volume of 1.0 ml/m3(actual amount: 87 ml). After 24 h of gas generation, the viable cell counts were determined as log10 CFU per disc. Three independent experiments were performed, and data represent mean ± SD (n=3). * P<0.05, significantly different from control discs treated without ClO2 gas (Student’s t-test).