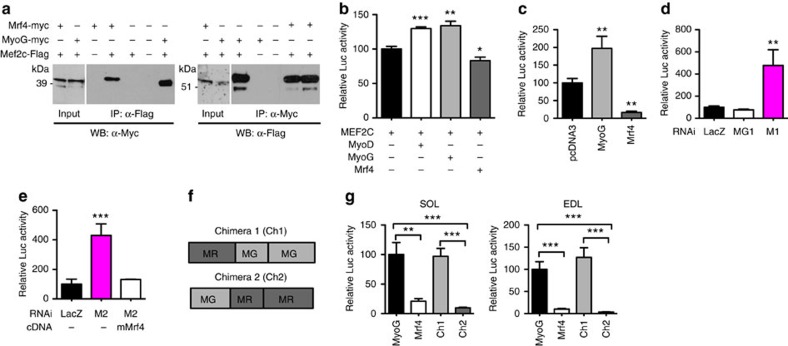
Figure 4. MRF4 physically interacts with MEF2 and inhibits its transcriptional activity.
(a) HEK-293 cells were transfected with MEF2C-Flag and co-transfected with myc-tagged MRF4 or myc-tagged myogenin (MyoG). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody and resolved by SDS–PAGE, followed by western blotting with anti-Myc antibody. MRF4, like MyoG, is co-immunoprecipitated with MEF2, and MEF2 is co-immunoprecipitated with MRF4 or MyoG. (b) HEK-293 cells co-transfected with MEF2C, a MEF2-Luciferase reporter, containing three tandem copies of the MEF2 site linked to luciferase, and either MyoD, myogenin or MRF4 (n=3). (c) Adult SOL muscle transfected with a MEF2-Luciferase reporter were co-transfected with Mrf4 or myogenin (n=4). (d) Adult SOL muscle transfected with a MEF2-Luciferase reporter were co-transfected with Mrf4 RNAi (M1) or myogenin RNAi (MG1) (n=4). (e) Adult SOL muscle transfected with a MEF2-Luciferase reporter were co-transfected with Mrf4 RNAi (M2) in the presence or absence of the M2-resistant mouse Mrf4 (mMrf4) (n=4). (f) Structure of two MRF4-myogenin chimeras containing either the N-terminal domain of MRF4 (MR) and the C-terminal domain of myogenin (MG) (chimera 1), or the N-terminal domain of myogenin and the C-terminal domain of MRF4 (chimera 2). (g) SOL and EDL muscles were transfected with the MEF2 reporter and co-transfected with either myogenin, Mrf4 or chimeric transgenes (n=5). Data are presented as means±s.e.m. from at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's two-tailed t-test (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).