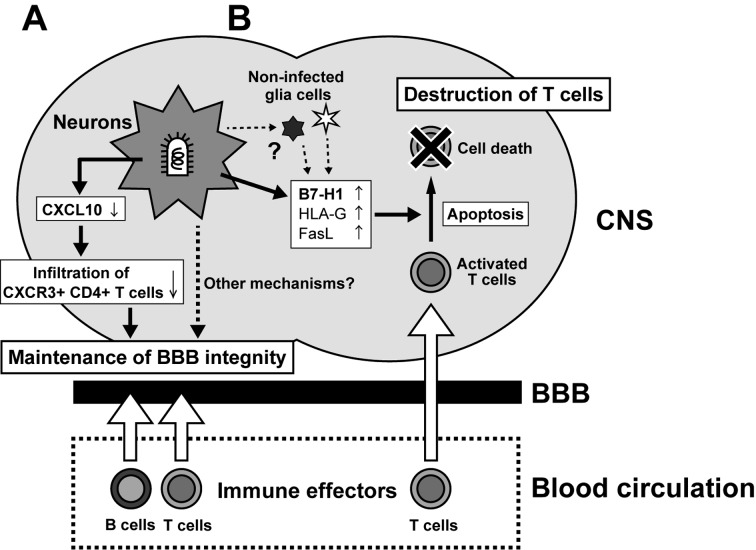
Fig. 3.
Summary of the two mechanisms proposed to effect suppression of neuroinflammation by RABV. (A) Infection of neurons by pathogenic but not attenuated RABV suppresses induction of CXCL10 expression, reducing CXCL10-dependent infiltration of CXCR3+ CD4+ T cells, thereby preventing transition to IL17-producing Th17 cells that promote BBB permeability and immune cell infiltration. (B) RABV infection induces expression of B7-H1 and other immunosuppressive molecules on infected neurons (and potentially non-infected glia), which induce the apoptosis of infiltrating T cells.