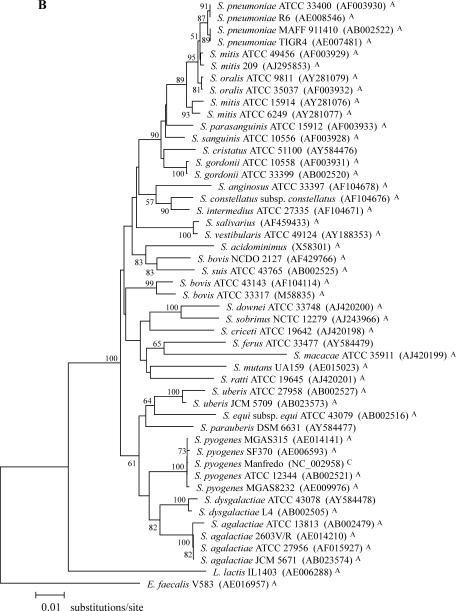
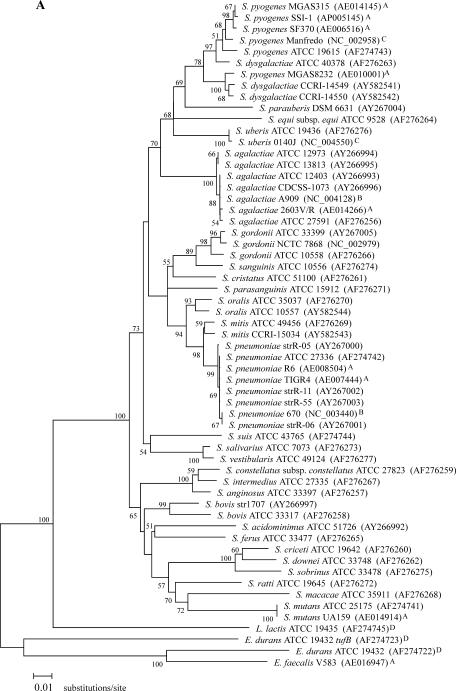
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic relationships among 28 streptococcal species. (A) Phylogenetic tree based on a 761-bp portion of tuf. (B) Phylogenetic tree based on a 1,260-bp portion of 16S rDNA. The trees were generated using the MEGA2 heuristic method, and evolutionary distance values were calculated by Kimura's two-parameter substitution model. The value on each branch represents the percentage of bootstrap replications supporting the branch. A total of 1,000 bootstrap replications were calculated. Bootstrap values lower than 50% are not shown. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. The tuf and 16S rDNA portions correspond to nucleotide positions 340 to 1,100 of the complete tuf gene of S. pneumoniae R6 (AE008504) and 93 to 1,382 of the complete 16S rRNA gene of S. pneumoniae R6 (AE008546). All sequences used for these phylogenetic analysis were obtained either from this study or from the following sources: GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) (A), TIGR ongoing genome projects (http://www.tigr.org) (B), Sanger ongoing genome projects (http://www.sanger.ac.uk) (C), and our group (for previously determined sequences) (24) (D); sequences from these four sources are indicated with A, B, C, and D, respectively.