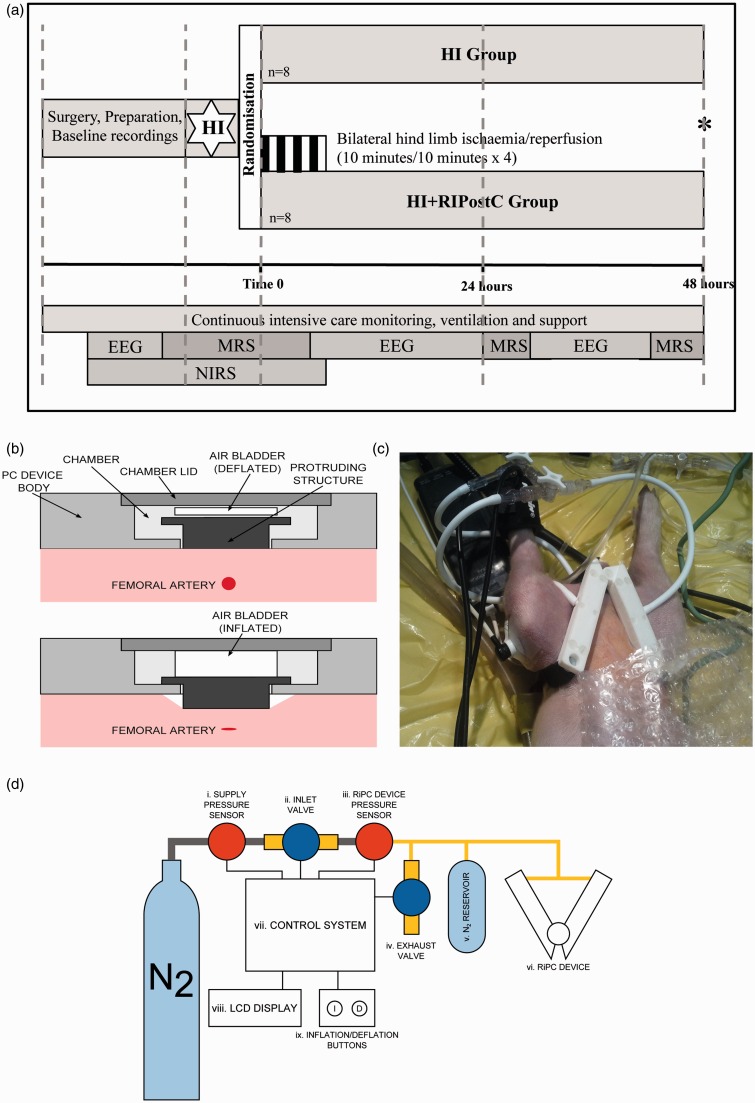
Figure 1.
(a). Study time-line. Following baseline data acquisition, piglets underwent cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. At the end of hypoxia-ischemia (time 0), piglets were randomized to (i) HI or (ii) HI + RIPostC. RIPostC was started immediately at Time 0. Piglets (Continued) Figure 1. Continue. were maintained under meticulous intensive care for 48 h at which point (*) they were euthanized. MRS was acquired at baseline, during HI, for the first 60 min after HI, and at 24 and 48 h. NIRS was acquired at baseline, during HI and throughout the four RIPostC cycles. EEG was acquired at baseline and in between the MRS acquisitions. (b) Side view of the RIPostC device remotely controlled in the bore of the 9.4 Tesla MR system. The top panel shows the device during the reperfusion period with the occluder in its resting position. The lower panel shows the inflated air bladder pushing the occluder forward to compress the femoral artery lying below. (c) The occluders are shown here with occlusion of both femoral arteries inducing lower limb ischemia. The lower limbs are clearly cyanosed. Limb ischemia was further confirmed by loss of the signal from the pulse oximeter and laser doppler in both limbs. (d) Diagram showing the complete RIPostC system used to remotely occlude both femoral arteries in the magnet. The closed system was connected to a nitrogen gas cylinder; pressure sensors allowed the gas pressure to be measured. The device was controlled by the inflation buttons, which allowed gas to enter the system, inflate the bladders, and occlude the femoral arteries.