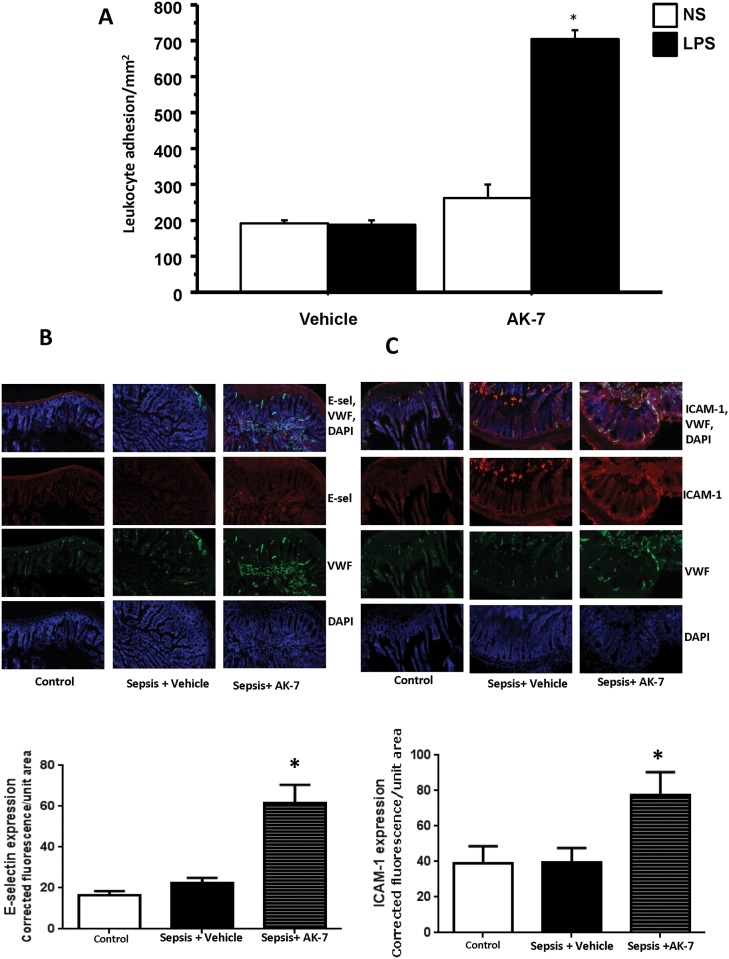
Fig 5. SIRT-2 inhibition in ob/ob septic mice restores repressed microvascular leukocyte adhesion.
A: SIRT-2 inhibition during hypo-inflammation enhances leukocyte adhesion in ob/ob: mice with sepsis: ob/ob-septic mice were treated with Vehicle or AK-7 during hypo-inflammatory phase of sepsis, challenged with either normal saline (NS) or LPS and studied leukocyte adhesion 4h later. While Vehicle treated mice showed no further increase in leukocyte adhesion in response to LPS, AK-7 treated mice showed significant increase in leukocyte adhesion in small intestinal microcirculation. * p<0.05 vs. Vehicle +LPS using Tukey‘s post-hoc analysis; error bars: s.e.m. B and C: SIRT-2 inhibition during hypo-inflammatory phase activates endothelium: We treated ob/ob mice with either Vehicle of AK-7 during hypo-inflammatory phase of sepsis and studied small intestinal tissue expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1 expression. We co-stained these tissue sections with wither von Willebrand factor or nuclear stain DAPI. We quantified the signal using NIH Image J. There was a significant increase in E-selectin (Fig 5B) and ICAM-1 (Fig 5C) expression in small intestinal tissue sections of Sepsis + AK-7 treated group compared to Sepsis + Vehicle group. * p<0.05 vs. Sepsis + Vehicle using Tukey‘s post-hoc analysis; error bars: s.e.m.